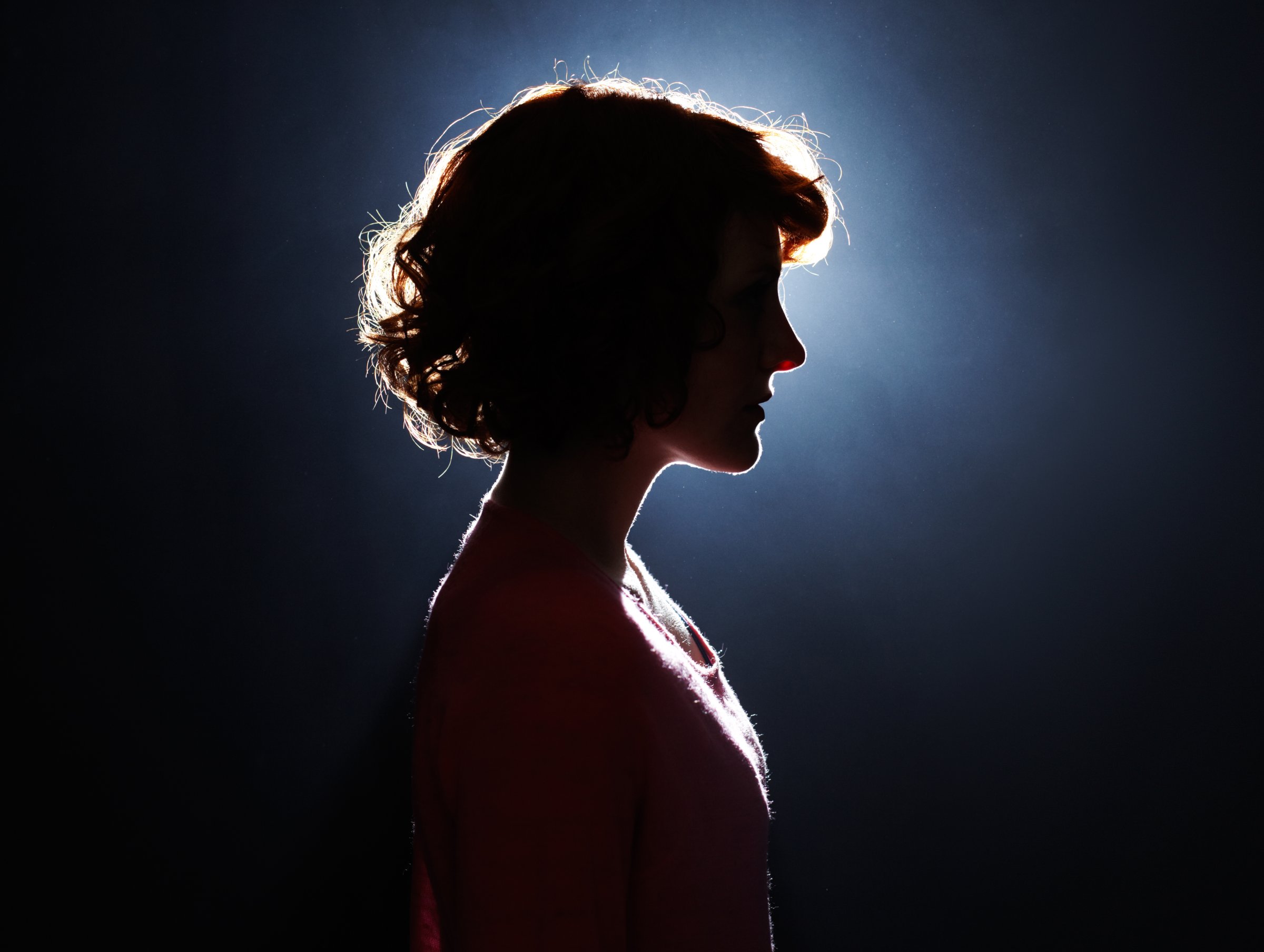

Feeling down every so often is a normal part of life. But when you’re gripped by an unrelenting sadness or hopelessness that keeps you from going about your usual routine, it’s time to pay attention: it’s the hallmark sign of clinical depression, and an estimated 7% of adults will experience it, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Even with this telltale sign in place, it’s tough for a depressed person to know if she really has the disease. “Almost all of the symptoms of depression on their own are experienced by everyone at one time or another,” explains Jennifer Payne, MD, director of the Women’s Mood Disorders Center at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore. If you’ve been dealing with the following symptoms every day for two weeks, and they’ve impaired the way you usually function (for example, prevented you from working, being a responsible parent, or seeing friends), it’s time to check in with your doctor.
HEALTH.COM: 10 Things to Say (and Not to Say) to Someone With Depression
You’re eating more (or less) than usual
Depression leaves you withdrawn and checked out, and that can manifest as a loss of appetite. “If your brain is preoccupied with negative thoughts, you may forget to eat or lose interest in cooking or preparing meals,” says Yvonne Thomas, PhD, Los Angeles-based psychologist specializing in depression and self-esteem. On the other hand, sometimes the disease kicks in the opposite effect, making you hungry and driving you to overeat. “The mix of emotions that tend to accompany depression—sadness, pessimism about the future, and low self-esteem—can compel you to try to soothe your feelings with food binges,” says Thomas.
You’re sleeping too much or too little
Some people with depression find themselves snoozing under the covers more; the disengagement and dip in energy make you fatigued, says Thomas. “Sleeping more is also a way depressed people escape from their sadness; it becomes a refuge,” she adds. Others with depression experience restless or interrupted sleep or even insomnia—they’re too wired by obsessive thoughts or ruminations to wind down and score the seven to eight hours per night most adults need. Thing is, not only can sleep changes be a tipoff to the disease, but they also make it worse. When you’re not getting the proper amount of shuteye, your body’s internal clock gets out of sync, and you’re even more tired and unfocused…and less able to cope.
HEALTH.COM: 7 Bedtime Behaviors That Will Help You Sleep
Small things agitate you
It’s a sneaky sign few people recognize: depression can show up as heightened irritability, says Jennifer Wolkin, PhD, clinical assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and anesthesiology at New York University’s Joan H. Tisch Center for Women’s Health. You might feel cranky and grumpy; little things that normally wouldn’t register set you off and leave you snapping at friends and coworkers. Part of the prickliness may be the way depression exacerbates normal hormonal swings. But it could also be triggered by the weight of so many heavy emotions. “When people are in physical pain, they often get angry and irritated easily, and it’s the same with psychological pain—you don’t feel good or like your usual self, and that saps your patience and puts you more on edge,” says Thomas.
You can’t concentrate or focus
Forgetting work deadlines or when to pick up your kids from a playdate? Feel like your mind resembles an out-of-focus photo, and the fuzziness has made a dent in the way you weigh choices and make decisions? That’s your brain on depression. Being preoccupied with thoughts of sadness and emptiness can plunge you into a head fog that affects your job, memory, and decision-making skills, says Wolkin. In turn, that unfocused thinking can lead you to make poor choices or take on unhealthy, risky behavior.
HEALTH.COM: 12 Unexpected Things That Mess With Your Memory
You don’t enjoy the things that once made you happy
You used to hit happy hour with your favorite group of coworkers, but for the last few weeks, you’ve been ducking out. Or you always looked forward to your nightly run, but these days, you can’t muster the interest. Not taking part in things you once enjoyed because they no longer give you pleasure is a telltale sign of depression. “A person who is simply blue might skip a few outings, then get back in the swing of things,” says Wolkin. “But depression makes you apathetic about activities and hobbies that once gave you joy, and that makes you isolate yourself.” It sets up that vicious cycle: depression robs you of your ability to derive pleasure from experiences, so you stop doing the very things that could brighten your mood.
HEALTH.COM: 12 Ways to Improve Your Concentration
10 Signs You Should See a Doctor for Depression originally appeared on Health.com.
See the 10 Healthiest Cities to Live in America








More Must-Reads from TIME
- Why Trump’s Message Worked on Latino Men
- What Trump’s Win Could Mean for Housing
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- Sleep Doctors Share the 1 Tip That’s Changed Their Lives
- Column: Let’s Bring Back Romance
- What It’s Like to Have Long COVID As a Kid
- FX’s Say Nothing Is the Must-Watch Political Thriller of 2024
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Contact us at letters@time.com