
The face of Tou Thao haunts me. The Hmong-American police officer stood with his back turned to Derek Chauvin, his partner, as Chauvin knelt on George Floyd’s neck for 8 minutes and 46 seconds and murdered him.
In the video that I saw, Tou Thao is in the foreground and Chauvin is partly visible in the background, George Floyd’s head pressed to the ground. Bystanders beg Tou Thao to do something, because George Floyd was not moving, and as he himself said, he could not breathe.
The face of Tou Thao is like mine and not like mine, although the face of George Floyd is like mine and not like mine too. Racism makes us focus on the differences in our faces rather than our similarities, and in the alchemical experiment of the U.S., racial difference mixes with labor exploitation to produce an explosive mix of profit and atrocity. In response to endemic American racism, those of us who have been racially stigmatized cohere around our racial difference. We take what white people hate about us, and we convert stigmata into pride, community and power. So it is that Tou Thao and I are “Asian Americans,” because we are both “Asian,” which is better than being an “Oriental” or a “gook.” If being an Oriental gets us mocked and being a gook can get us killed, being an Asian American might save us. Our strength in numbers, in solidarity across our many differences of language, ethnicity, culture, religion, national ancestry and more, is the basis of being Asian American.
But in another reality, Tou Thao is Hmong and I am Vietnamese. He was a police officer and I am a professor. Does our being Asian bring us together across these ethnic and class divides? Does our being Southeast Asian, both our communities brought here by an American war in our countries, mean we see the world in the same way? Did Tou Thao experience the anti-Asian racism that makes us all Asian, whether we want to be or not?
Let me go back in time to a time being repeated today. Even if I no longer remember how old I was when I saw these words, I have never forgotten them: Another American driven out of business by the Vietnamese. Perhaps I was 12 or 13. It was the early 1980s, and someone had written them on a sign in a store window not far from my parents’ store. The sign confused me, for while I had been born in Vietnam, I had grown up in Pennsylvania and California, and had absorbed all kinds of Americana: the Mayflower and the Pilgrims; cowboys and Indians; Audie Murphy and John Wayne; George Washington and Betsy Ross; the Pledge of Allegiance; the Declaration of Independence; the guarantee of life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness; all the fantasy and folklore of the American Dream.

Part of that dream was being against communism and for capitalism, which suited my parents perfectly. They had been born poor to rural families, and without much formal schooling and using only their ingenuity and hard work, had become successful merchants. They fled communist Vietnam in 1975, after losing all of their property and most of their fortune. What they carried with them–including some gold and money sewn into the hems of their clothes–they used to buy a house next to the freeway in San Jose and to open the second Vietnamese grocery store there, in 1978. In a burst of optimism and nostalgia, they named their store the New Saigon.
I am now older than my parents were when they had to begin their lives anew in this country, with only a little English. What they did looms in my memory as a nearly unimaginable feat. In the age of coronavirus, I am uncertain how to sew a mask and worry about shopping for groceries. Survivors of war, my parents fought to live again as aliens in a strange land, learning to read mortgage documents in another language, enrolling my brother and me in school, taking driver’s-license examinations. But there was no manual telling them how to buy a store that was not advertised as for sale. They called strangers and navigated bureaucracy in order to find the owners and persuade them to sell, all while suffering from the trauma of having lost their country and leaving almost all their relatives behind. By the time my parents bought the store, my mother’s mother had died in Vietnam. The news nearly broke her.
Somehow the person who wrote this sign saw people like my mother and my father as less than human, as an enemy. This is why I am not surprised by the rising tide of anti-Asian racism in this country. Sickened, yes, to hear of a woman splashed with acid on her doorstep; a man and his son slashed by a knife-wielding assailant at a Sam’s Club; numerous people being called the “Chinese virus” or the “chink virus” or told to go to China, even if they are not of Chinese descent; people being spat on for being Asian; people afraid to leave their homes, not only because of the pandemic but also out of fear of being verbally or physically assaulted, or just looked at askance. Cataloging these incidents, the poet and essayist Cathy Park Hong wrote, “We don’t have coronavirus. We are coronavirus.”
Looking back, I can remember the low-level racism of my youth, the stupid jokes told by my Catholic-school classmates, like “Is your last name Nam?” and “Did you carry an AK-47 in the war?” as well as more obscene ones. I wonder: Did Tou Thao hear these kinds of jokes in Minnesota? What did he think of Fong Lee, Hmong American, 19 years old, shot eight times, four in the back, by Minneapolis police officer Jason Andersen in 2006? Andersen was acquitted by an all-white jury.

Confronted with anti-Asian racism from white people, the Hmong who came to the U.S. as refugees in the 1970s and 1980s were often resettled in diverse urban areas, some in dominantly Black communities where they also confronted racism. “Stories abounded within our community of battery, robberies and intimidations by our Black neighbors,” Yia Vue wrote recently. “Hmong people live side by side with their African-American neighbors in poorer sections of town, with generations of misunderstanding and stereotypes still strongly entrenched on both sides.” Yet when Fong Lee was killed, Black activists rallied to his cause. “They were the loudest voices for us,” Lee’s sister Shoua said. “They didn’t ask to show up. They just showed up.”
Unlike the engineers and doctors who mostly came from Hong Kong, Taiwan, China and India–the model minority in the American imagination–many Hmong refugees arrived from a rural life in Laos devastated by war. Traumatized, they were resettled into the midst of poverty and a complicated history of racial oppression of which they had little awareness. Even the Hmong who condemn Tou Thao and argue for solidarity with Black Lives Matter insist that they should not be seen through the lens of the model-minority experience, should not be subject to liberal Asian-American guilt and hand-wringing over Tou Thao as a symbol of complicity. Christian minister Ashley Gaozong Bauer, of Hmong descent, writes, “We’ve had to share in the collective shame of the model minority, but when have Asian Americans shared in the pain and suffering of the Hmong refugee narrative and threats of deportation?”
Like the Hmong, the Vietnamese like myself suffered from war, and some are threatened by deportation now. Unlike many of the Hmong, a good number of Vietnamese refugees became, deliberately or otherwise, a part of the model minority, including myself. The low-level racism I experienced happened in elite environments. By the time I entered my mostly white, exclusive, private high school, the message was clear to me and the few of us who were of Asian descent. Most of us gathered every day in a corner of the campus and called ourselves, with a laugh, or maybe a wince, “the Asian invasion.” But if that was a joke we made at our own expense, it was also a prophecy, for when I returned to campus a couple of years ago to give a lecture on race to the assembled student body, some 1,600 young men, I realized that if we had not quite taken over, there were many more of us almost 30 years later. No longer the threat of the Asian invasion, we were, instead, the model minority: the desirable classmate, the favored neighbor, the nonthreatening kind of person of color.
Or were we? A couple of Asian-American students talked to me afterward and said they still felt it. The vibe. The feeling of being foreign, especially if they were, or were perceived to be, Muslim, or brown, or Middle Eastern. The vibe. Racism is not just the physical assault. I have never been physically assaulted because of my appearance. But I had been assaulted by the racism of the airwaves, the ching-chong jokes of radio shock jocks, the villainous or comical japs and chinks and gooks of American war movies and comedies. Like many Asian Americans, I learned to feel a sense of shame over the things that supposedly made us foreign: our food, our language, our haircuts, our fashion, our smell, our parents.
What made these sentiments worse, Hong argues, was that we told ourselves these were “minor feelings.” How could we have anything valid to feel or say about race when we, as a model minority, were supposedly accepted by American society? At the same time, anti-Asian sentiment remained a reservoir of major feeling from which Americans could always draw in a time of crisis. Asian Americans still do not wield enough political power, or have enough cultural presence, to make many of our fellow Americans hesitate in deploying a racist idea. Our unimportance and our historical status as the perpetual foreigner in the U.S. is one reason the President and many others feel they can call COVID-19 the “Chinese virus” or the “kung flu.”

The basis of anti-Asian racism is that Asians belong in Asia, no matter how many generations we have actually lived in non-Asian countries, or what we might have done to prove our belonging to non-Asian countries if we were not born there. Pointing the finger at Asians in Asia, or Asians in non-Asian countries, has been a tried and true method of racism for a long time; in the U.S., it dates from the 19th century.
It was then that the U.S. imported thousands of Chinese workers to build the transcontinental railroad. When their usefulness was over, American politicians, journalists and business leaders demonized them racially to appease white workers who felt threatened by Chinese competition. The result was white mobs lynching Chinese migrants, driving them en masse out of towns and burning down Chinatowns. The climax of anti-Chinese feeling was the passage of the 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act, the first racially discriminatory immigration law in American history, which would turn Chinese entering the U.S. into the nation’s first illegal immigrant population. The Immigration and Naturalization Service was created, policing Chinese immigration and identifying Chinese who had come into the U.S. as “paper sons,” who claimed a fictive relation to the Chinese who had already managed to come into the country. As the political scientist Janelle Wong tells me, while “European immigrants were confronted with widespread hostility, they never faced the kind of legal racial restrictions on immigration and naturalization that Asian Americans experienced.”
American history has been marked by the cycle of big businesses relying on cheap Asian labor, which threatened the white working class, whose fears were stoked by race-baiting politicians and media, leading to catastrophic events like the Chinese Exclusion Act and the internment of Japanese Americans in 1942. The person who wrote that sign I remember seeing as a child, blaming the Vietnamese for destroying American businesses, was simply telling a story about the yellow peril that was always available for fearful Americans.
The reality was that downtown San Jose in the 1970s and 1980s was shabby, a run-down place where almost no one wanted to open new businesses, except for Vietnamese refugees. Today, Americans rely on China and other Asian countries for cheap commodities that help Americans live the American Dream, then turn around and blame the Chinese for the loss of American jobs or the rise of American vulnerability to economic competition.
It is easier to blame a foreign country or a minority, or even politicians who negotiate trade agreements, than to identify the real power: corporations and economic elites who shift jobs, maximize profit at the expense of workers and care nothing for working Americans. To acknowledge this reality is far too disturbing for many Americans, who resort to blaming Asians as a simpler answer. Asian Americans have not forgotten this anti-Asian history, and yet many have hoped that it was behind them. The slur of the “Chinese virus” has revealed how fragile our acceptance and inclusion was.
In the face of renewed attacks on our American belonging, the former presidential candidate Andrew Yang offered this solution: “We Asian Americans need to embrace and show our Americanness in ways we never have before … We should show without a shadow of a doubt that we are Americans who will do our part for our country in this time of need.” Many Asian Americans took offense at his call, which seemed to apologize for our Asian-American existence. Yang’s critics pointed out that Asian Americans have literally wrapped themselves in the American flag in times of anti-Asian crisis; have donated to white neighbors and fellow citizens in emergencies; and died for this country fighting in its wars. And is there anything more American than joining the police? Did Tou Thao think he was proving his belonging by becoming a cop?
None of these efforts have prevented the stubborn persistence of anti-Asian racism. Calling for more sacrifices simply reiterates the sense that Asian Americans are not American and must constantly prove an Americanness that should not need to be proven. Japanese Americans had to prove their Americanness during World War II by fighting against Germans and Japanese while their families were incarcerated, but German and Italian Americans never had to prove their Americanness to the same extent. German and Italian Americans were selectively imprisoned for suspected or actual disloyalty, while Japanese Americans were incarcerated en masse, their race marking them as un-American.
Asian Americans are caught between the perception that we are inevitably foreign and the temptation that we can be allied with white people in a country built on white supremacy. As a result, anti-Black (and anti-brown and anti-Native) racism runs deep in Asian-American communities. Immigrants and refugees, including Asian ones, know that we usually have to start low on the ladder of American success. But no matter how low down we are, we know that America allows us to stand on the shoulders of Black, brown and Native people. Throughout Asian-American history, Asian immigrants and their descendants have been offered the opportunity by both Black people and white people to choose sides in the Black-white racial divide, and we have far too often chosen the white side. Asian Americans, while actively critical of anti-Asian racism, have not always stood up against anti-Black racism. Frequently, we have gone along with the status quo and affiliated with white people.

And yet there have been vocal Asian Americans who have called for solidarity with Black people and other people of color, from the activist Yuri Kochiyama, who cradled a dying Malcolm X, to the activist Grace Lee Boggs, who settled in Detroit and engaged in serious, radical organizing and theorizing with her Black husband James Boggs. Kochiyama and Lee Boggs were far from the only Asian Americans who argued that Asian Americans should not stand alone or stand only for themselves. The very term Asian American, coined in the 1960s by Yuji Ichioka and Emma Gee and adopted by college student activists, was brought to national consciousness by a movement that was about more than just defending Asian Americans against racism and promoting an Asian-American identity.
Asian-American activists saw their movement as also being antiwar, anti-imperialism and anticapitalism. Taking inspiration from the 1955 Bandung Conference, a gathering of nonaligned African and Asian nations, and from Mao, they located themselves in an international struggle against colonialism with other colonized peoples. Mao also inspired radical African Americans, and the late 1960s in the U.S. was a moment when radical activists of all backgrounds saw themselves as part of a Third World movement that linked the uprisings of racial minorities with a global rebellion against capitalism, racism, colonialism and war.
The legacy of the Third World and Asian-American movements continues today among Asian-American activists and scholars, who have long argued that Asian Americans, because of their history of experiencing racism and labor exploitation, offer a radical potential for contesting the worst aspects of American society. But the more than 22 million Asian Americans, over 6% of the American population, have many different national and ethnic origins and ancestries and times of immigration or settlement. As a result, we often have divergent political viewpoints. Today’s Asian Americans are being offered two paths: the radical future imagined by the Asian-American movement, and the consumer model symbolized by drinking boba tea and listening to K-pop. While Asian Americans increasingly trend Democratic, we are far from all being radical.
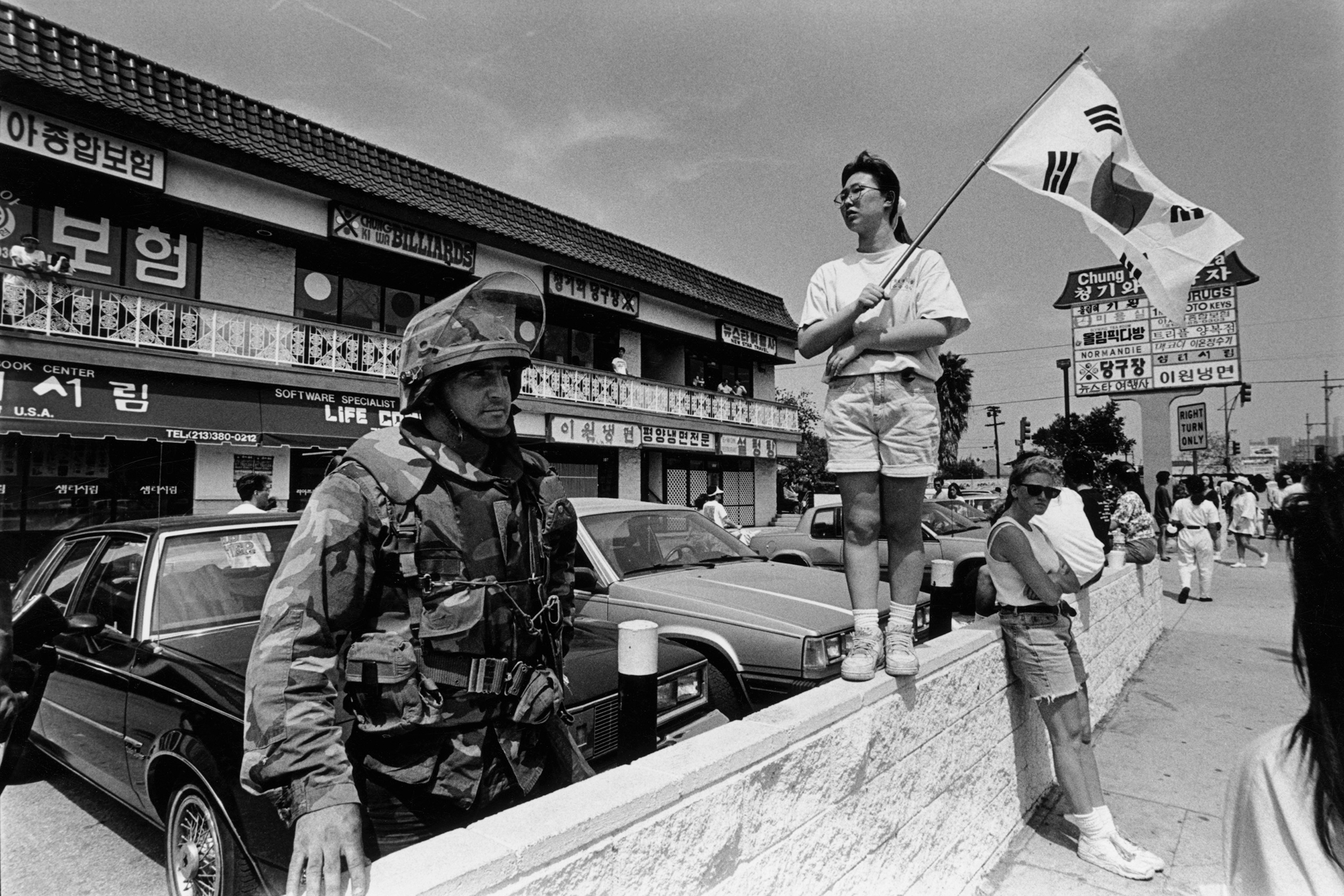
What usually unifies Asian Americans and enrages us is anti-Asian racism and murder, beginning with the anti-Chinese violence and virulence of the 19th century and continuing through incidents like a white gunman killing five Vietnamese and Cambodian refugee children in a Stockton, Calif., school in 1989, and another white gunman killing six members of a Sikh gurdwara in Wisconsin in 2012. The murder of Vincent Chin, killed in 1982 by white Detroit autoworkers who mistook him for Japanese, remains a rallying cry. As do the Los Angeles riots, or uprisings, of 1992, when much of Koreatown was burned down by mostly Black and brown looters while the LAPD watched. Korean-American merchants suffered about half of the economic damage. Two Asian Americans were killed in the violence.
All of this is cause for mourning, remembrance and outrage, but so is something else: the 61 other people who died were not Asian, and the majority of them were Black or brown. Most of the more than 12,000 people who were arrested were also Black or brown. In short, Korean Americans suffered economic losses, as well as emotional and psychic damage, that would continue for years afterward. But they had property to lose, and they did not pay the price of their tenuous Americanness through the same loss of life or liberty as experienced by their Black and brown customers and neighbors.
Many Korean Americans were angry because they felt the city’s law-enforcement and political leadership had sacrificed them by preventing the unrest from reaching the whiter parts of the city, making Korean Americans bear the brunt of the long-simmering rage of Black and brown Angelenos over poverty, segregation and abusive police treatment. In the aftermath, Koreatown was rebuilt, although not all of the shopkeepers recovered their livelihoods. Some of the money that rebuilt Koreatown came, ironically, from South Korea, which had enjoyed a decades-long transformation into an economic powerhouse. South Korean capital, and eventually South Korean pop culture, especially cinema and K-pop, became cooler and more fashionable than the Korean immigrants who had left South Korea for the American Dream. Even if economic struggle still defined a good deal of Korean immigrant life, it was overshadowed by the overall American perception of Asian-American success, and by the new factor of Asian capital and competition.
This is what it means to be a model minority: to be invisible in most circumstances because we are doing what we are supposed to be doing, like my parents, until we become hypervisible because we are doing what we do too well, like the Korean shopkeepers. Then the model minority becomes the Asian invasion, and the Asian-American model minority, which had served to prove the success of capitalism, bears the blame when capitalism fails.

Not to say that we bear the brunt of capitalism. Situated in the middle of America’s fraught racial relations, we receive, on the whole, more benefits from American capitalism than Black, brown or Indigenous peoples, even if many of us also experience poverty and marginalization. While some of us do die from police abuse, it does not happen on the same scale as that directed against Black, brown or Indigenous peoples. While we do experience segregation and racism and hostility, we are also more likely to live in integrated neighborhoods than Black or Indigenous people. To the extent that we experience advantage because of our race, we are also complicit in holding up a system that disadvantages Black, brown and Indigenous people because of their race.
Given our tenuous place in American society, no wonder so many Asian Americans might want to prove their Americanness, or to dream of acceptance by a white-dominated society, or condemn Tou Thao as not one of “us.” But when Asian Americans speak of their vast collective, with origins from East to West Asia and South to Southeast Asia, who is the “we” that we use? The elite multiculturalism of colored faces in high places is a genteel politics of representation that focuses on assimilation. So long excluded from American life, marked as inassimilable aliens and perpetual foreigners, asked where we come from and complimented on our English, Asian immigrants and their descendants have sought passionately to make this country our own. But from the perspective of many Black, brown and Indigenous people, this country was built on their enslavement, their dispossession, their erasure, their forced migration, their imprisonment, their segregation, their abuse, their exploited labor and their colonization.
For many if not all Black, brown and Indigenous people, the American Dream is a farce as much as a tragedy. Multiculturalism may make us feel good, but it will not save the American Dream; reparations, economic redistribution, and defunding or abolishing the police might.
If Hmong experiences fit more closely with the failure of the American Dream, what does it mean for some Asian Americans to still want their piece of it? If we claim America, then we must claim all of America, its hope and its hypocrisy, its profit and its pain, its liberty and its losses, its imperfect union and its ongoing segregation.
To be Asian American is therefore paradoxical, for being Asian American is both necessary and insufficient. Being Asian American is necessary, the name and identity giving us something to organize around, allowing us to have more than “minor feelings.” I vividly remember becoming an Asian American in my sophomore year, when I transferred to UC Berkeley, stepped foot on the campus and was immediately struck by intellectual and political lightning. Through my Asian-American studies courses and my fellow student activists of the Asian American Political Alliance, I was no longer a faceless part of an “Asian invasion.” I was an Asian American. I had a face, a voice, a name, a movement, a history, a consciousness, a rage. That rage is a major feeling, compelling me to refuse a submissive politics of apology, which an uncritical acceptance of the American Dream demands.
But the rage that is at the heart of the Asian-American movement–a righteous rage, a wrath for justice, acknowledgment, redemption–has not been able to overcome the transformation of the movement into a diluted if empowering identity. In its most diluted form, Asian-American identity is also open to anti-Black racism, the acceptance of colonization, and the fueling of America’s perpetual-motion war machine, which Americans from across the Democratic and Republican parties accept as a part of the U.S.
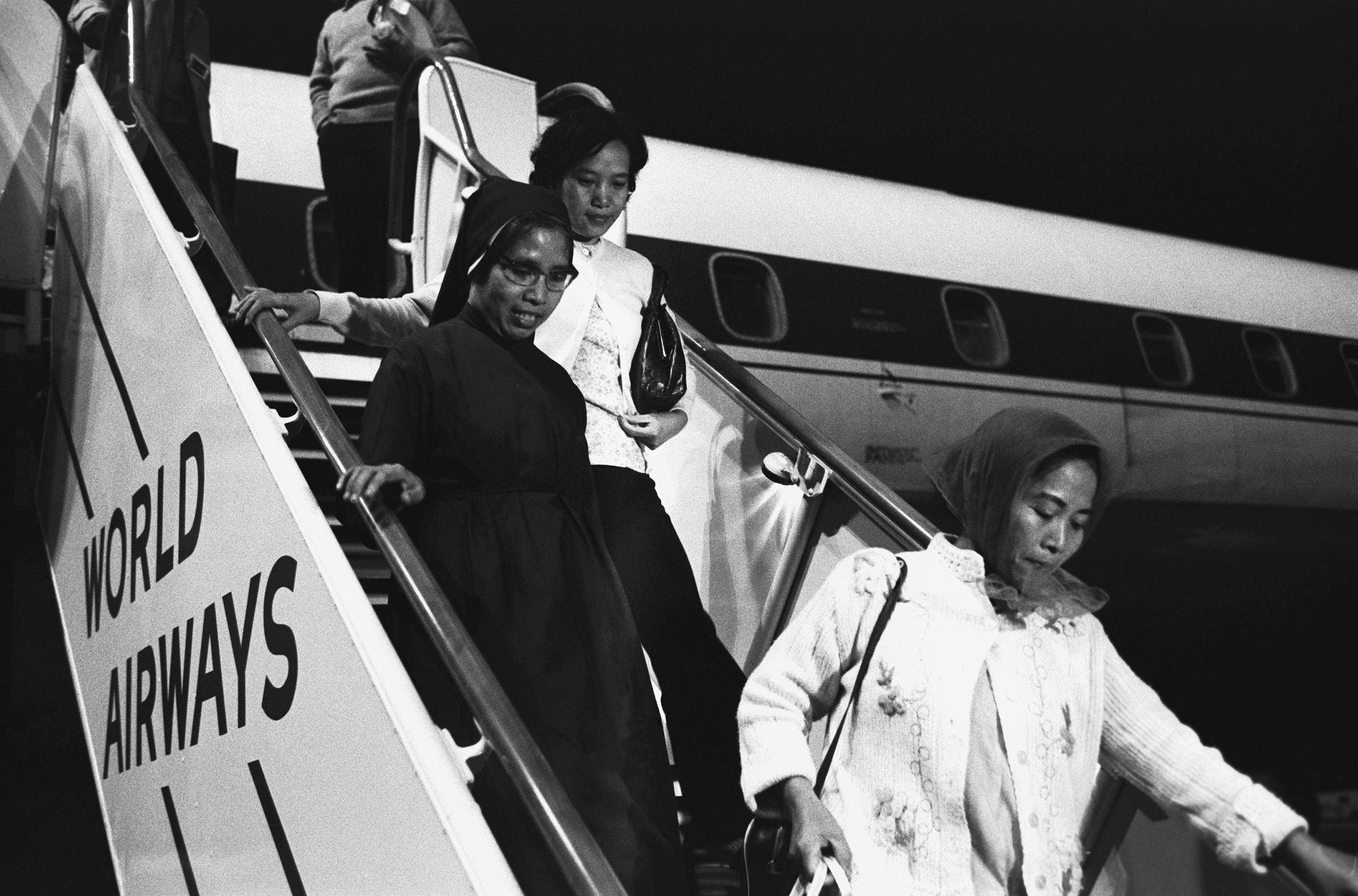

My presence here in this country, and that of my parents, and a majority of Vietnamese and Hmong, is due to the so-called Vietnam War in Southeast Asia that the U.S. helped to wage. The war in Laos was called “the Secret War” because the CIA conducted it and kept it secret from the American people. In Laos, the Hmong were a stateless minority without a country to call their own, and CIA advisers promised the Hmong that if they fought along with them, the U.S. would take care of the Hmong in both victory and defeat, perhaps even helping them gain their own homeland. About 58,000 Hmong who fought with the Americans lost their lives, fighting communists and rescuing downed American pilots flying secret bombing missions over Laos. When the war ended, the CIA abandoned most of its Hmong allies, taking only a small number out of the country to Thailand. The ones who remained behind suffered persecution at the hands of their communist enemies.
This is why Tou Thao’s face haunts me. Not just because we may look alike in some superficial way as Asian Americans, but because he and I are here because of this American history of war. The war was a tragedy for us, as it was for the Black Americans who were sent to “guarantee liberties in Southeast Asia which they had not found in southwest Georgia and East Harlem,” as Martin Luther King Jr. argued passionately in his 1967 speech “Beyond Vietnam.” In this radical speech, he condemns not just racism but capitalism, militarism, American imperialism and the American war machine, “the greatest purveyor of violence in the world today.” In another speech, he demands that we question our “whole society,” which means “ultimately coming to see that the problem of racism, the problem of economic exploitation and the problem of war are all tied together.”
Little has changed. The U.S. is still a country built on war and for war. This is why “Vietnam,” meaning the Vietnam War, continues to haunt this country, stuck in a forever war. And this is why Tou Thao’s face haunts me. It is the face of someone who shares some of my history and has done the thing I fear to do when faced with injustice–nothing. Addressing Tou Thao, the poet Mai Der Vang, also Hmong, wrote in her poem “In the Year of Permutations”: “Go live with yourself after what you didn’t do.” Thao was “complicit in adding to the/ perpetration of power on a neck … Never truly to be accepted/ always a pawn.” While the life of a Hmong-American police officer descended from refugees is different from that of a stereotypical model-minority Chinese-American engineer or a Vietnamese-American writer like me, the moral choices remain the same. Solidarity or complicity. Rise against abusive power or stand with our back turned to the abuse of power. If we as Asian Americans choose the latter, we are indeed the model minority, and we deserve both its privileges and its perils.
Our challenge is to be both Asian American and to imagine a world beyond it, one in which being Asian American isn’t necessary. This is not a problem of assimilation or multiculturalism. This is a contradiction, inherited from the fundamental contradiction that ties the American body politic together, its aspiration toward equality for all, bound with its need to exploit the land and racially marked people, beginning from the very origins of American society and its conquest of Indigenous nations and importation of African slaves. The U.S. is an example of a successful project of colonization, only we do not call colonization by that name here. Instead, we call successful colonization “the American Dream.” This is why, as Mai Der Vang says, “the American Dream will not save us.”
“Asian Americans” should not exist in a land where everyone is equal, but because of racism’s persistence, and capitalism’s need for cheap, racialized labor, “Asian Americans” do indeed exist. The end of Asian Americans only happens with the end of racism and capitalism. Faced with this problem, Asian Americans can be a model of apology, trying to prove an Americanness that cannot be proved. Or we can be a model of justice and demand greater economic and social equality for us and for all Americans.
If we are dissatisfied with our country’s failures and limitations, revealed to us in stark clarity during the time of coronavirus, then now is our time to change our country for the better. If you think America is in trouble, blame shareholders, not immigrants; look at CEOs, not foreigners; resent corporations, not minorities; yell at politicians of both parties, not the weak, who have little in the way of power or wealth to share. Many Americans of all backgrounds understand this better now than they did in 1992. Then, angry protesters burned down Koreatown. Now, they peacefully surround the White House.
Demanding that the powerful and the wealthy share their power and their wealth is what will make America great. Until then, race will continue to divide us. To locate Tou Thao in the middle of a Black-Hmong divide, or a Black-Asian divide, as if race were the only problem and the only answer, obscures a fatal statistic: the national poverty rate was 15.1% in 2015, while the rate for African Americans was about 24.1% and for Hmong Americans 28.3%.
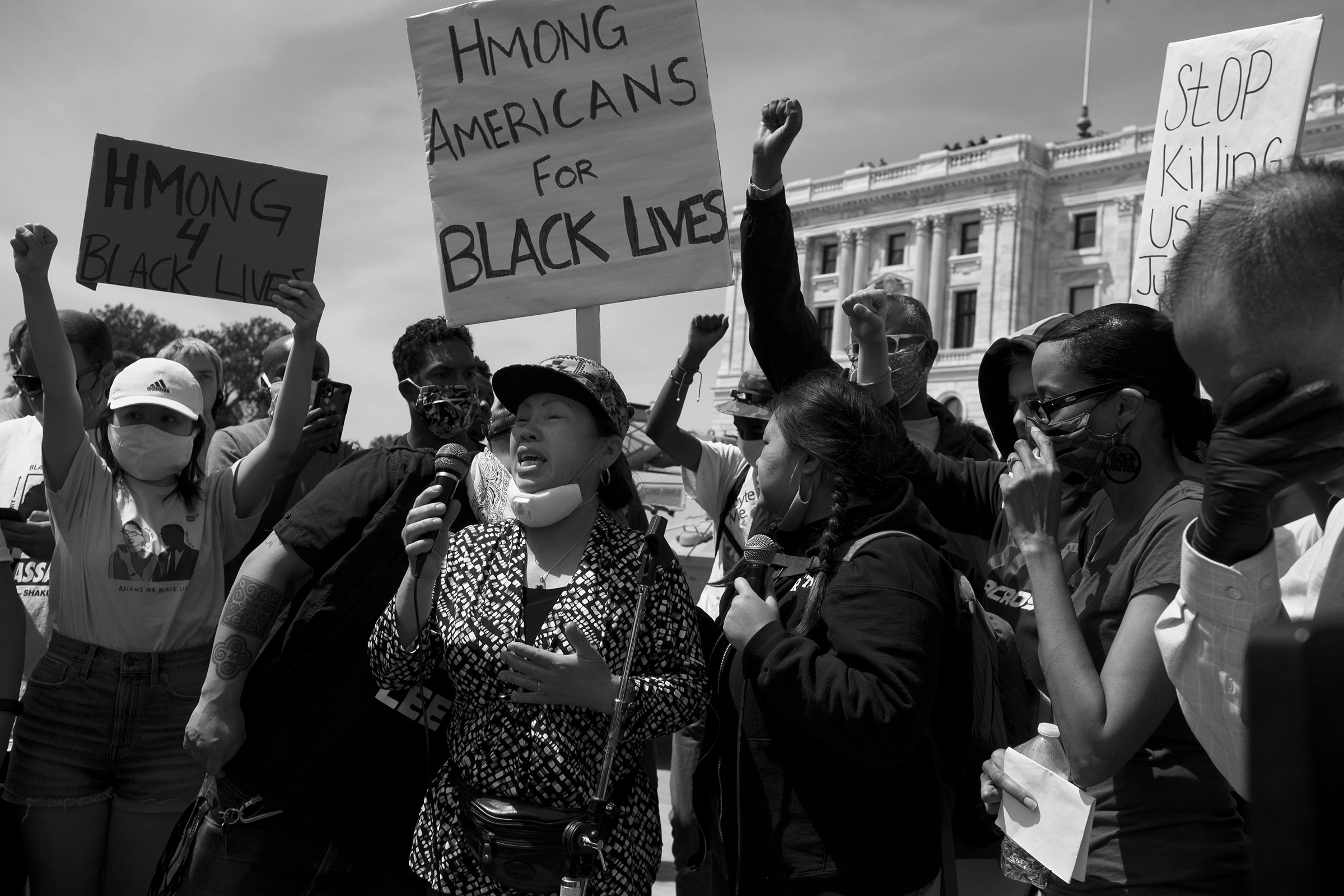
The problem is race, and class, and war–a country almost always at war overseas that then pits its poor of all races and its exploited minorities against each other in a domestic war over scarce resources. So long as this crossbred system of white supremacy and capitalist exploitation remains in place, there will always be someone who will write that sign: Another American Driven Out of Business by [fill in the blank], because racism always offers the temptation to blame the weak rather than the powerful. The people who write these signs are engaging in the most dangerous kind of identity politics, the nationalist American kind, which, from the origins of this country, has been white and propertied. The police were created to defend the white, the propertied and their allies, and continue to do so. Black people know this all too well, many descended from people who were property.
My parents, as newcomers to America, learned this lesson most intimately. When they opened the New Saigon, they told me not to call the police if there was trouble. In Vietnam, the police were not to be trusted. The police were corrupt. But a few years later, when an armed (white) gunman burst into our house and pointed a gun in all our faces, and after my mother dashed by him and into the street and saved our lives, I called the police. The police officers who came were white and Latino. They were gentle and respectful with us. We owned property. We were the victims. And yet our status as people with property, as refugees fulfilling the American Dream, as good neighbors for white people, is always fragile, so long as that sign can always be hung.
But the people who would hang that sign misunderstand a basic fact of American life: America is built on the business of driving other businesses out of business. This is the life cycle of capitalism, one in which an (Asian) American Dream that is multicultural, transpacific and corporate fits perfectly well. My parents, natural capitalists, succeeded at this life cycle until they, in turn, were driven out of business. The city of San Jose, which had neglected downtown when my parents arrived, changed its approach with the rise of Silicon Valley. Realizing that downtown should reflect the image of a modern tech metropolis, the city used eminent domain to force my parents to sell their store. Across from where the New Saigon once stood now looms the brand-new city hall, which was supposed to face a brand-new symphony hall.
I love the idea that a symphony could have sprung from the refugee roots of the New Saigon, where my parents shed not only sweat but blood, having once been shot there on Christmas Eve. But for many years, all that stood on my parents’ property was a dismal parking lot. Eventually the city sold the property for many millions of dollars, and now a tower of expensive condominiums is being built on the site of my parents’ struggle for the American Dream. The symphony was never heard. This, too, is America.
So is this: the mother of Fong Lee, Youa Vang Lee, marching with Hmong 4 Black Lives on the Minnesota state capitol in the wake of George Floyd’s killing. “I have to be there,” she said. She spoke in Hmong, but her feelings could be understood without translation.
“The same happened to my son.”
Nguyen is a Pulitzer Prize–winning novelist and a University Professor at the University of Southern California
Correction, June 29, 2020
The original version of this story misstated the spelling of the last name of the police officer who killed Fong Lee. It is Andersen, not Anderson.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Donald Trump Is TIME's 2024 Person of the Year
- Why We Chose Trump as Person of the Year
- Is Intermittent Fasting Good or Bad for You?
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- The 20 Best Christmas TV Episodes
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Contact us at letters@time.com