
Not long after Nelly Spigner arrived at the University of Richmond in 2014 as a Division I soccer player and aspiring surgeon, college began to feel like a pressure cooker. Overwhelmed by her busy soccer schedule and heavy course load, she found herself fixating on how each grade would bring her closer to medical school. “I was running myself so thin trying to be the best college student,” she says. “It almost seems like they’re setting you up to fail because of the sheer amount of work and amount of classes you have to take at the same time, and how you’re also expected to do so much.”
At first, Spigner hesitated to seek help at the university’s counseling center, which was conspicuously located in the psychology building, separate from the health center. “No one wanted to be seen going up to that office,” she says. But she began to experience intense mood swings. At times, she found herself crying uncontrollably, unable to leave her room, only to feel normal again in 30 minutes. She started skipping classes and meals, avoiding friends and professors, and holing up in her dorm. In the spring of her freshman year, she saw a psychiatrist on campus, who diagnosed her with bipolar disorder, and her symptoms worsened. The soccer team wouldn’t allow her to play after she missed too many practices, so she left the team. In October of her sophomore year, she withdrew from school on medical leave, feeling defeated. “When you’re going through that and you’re looking around on campus, it doesn’t seem like anyone else is going through what you’re going through,” she says. “It was probably the loneliest experience.”
Spigner is one of a rapidly growing number of college students seeking mental health treatment on campuses facing an unprecedented demand for counseling services. Between 2009 and 2015, the number of students visiting counseling centers increased by about 30% on average, while enrollment grew by less than 6%, the Center for Collegiate Mental Health found in a 2015 report. Students seeking help are increasingly likely to have attempted suicide or engaged in self-harm, the center found. In spring 2017, nearly 40% of college students said they had felt so depressed in the prior year that it was difficult for them to function, and 61% of students said they had “felt overwhelming anxiety” in the same time period, according to an American College Health Association survey of more than 63,000 students at 92 schools.
As midterms begin in March, students’ workload intensifies, the wait time for treatment at counseling centers grows longer, and students who are still struggling to adjust to college consider not returning after the spring or summer breaks. To prevent students from burning out and dropping out, colleges across the country — where health centers might once have left meaningful care to outside providers — are experimenting with new measures. For the first time last fall, UCLA offered all incoming students a free online screening for depression. More than 2,700 students have opted in, and counselors have followed up with more than 250 who were identified as being at risk for severe depression, exhibiting manic behavior or having suicidal thoughts.
Virginia Tech University has opened several satellite counseling clinics to reach students where they already spend time, stationing one above a local Starbucks and embedding others in the athletic department and graduate student center. Ohio State University added a dozen mental health clinicians during the 2016-17 academic year and has also launched a counseling mobile app that allows students to make an appointment, access breathing exercises, listen to a playlist designed to cheer them up, and contact the clinic in case of an emergency. Pennsylvania State University allocated roughly $700,000 in additional funding for counseling and psychological services in 2017, citing a “dramatic increase” in the demand for care over the past 10 years. And student government leaders at several schools have enacted new student fees that direct more funding to counseling centers.
But most counseling centers are working with limited resources. The average university has one professional counselor for every 1,737 students — fewer than the minimum of one therapist for every 1,000 to 1,500 students recommended by the International Association of Counseling Services. Some counselors say they are experiencing “battle fatigue” and are overwhelmed by the increase in students asking for help. “It’s a very different job than it was 10 years ago,” says Lisa Adams Somerlot, president of the American College Counseling Association and director of counseling at the University of West Georgia.
As colleges try to meet the growing demand, some students are slipping through the cracks due to long waits for treatment and a lasting stigma associated with mental health issues. Even if students ask for and receive help, not all cases can be treated on campus. Many private-sector treatment programs are stepping in to fill that gap, at least for families who can afford steep fees that may rise above $10,000 and may not be covered by health insurance. But especially in rural areas, where options for off-campus care are limited, universities are feeling pressure to do more.
‘I needed something the university wasn’t offering’
At the start of every school year, Anne Marie Albano, director of the Columbia University Clinic for Anxiety and Related Disorders (CUCARD), says she’s inundated with texts and phone calls from students who struggle with the transition to college life. “Elementary and high school is so much about right or wrong,” she says. “You get the right answer or you don’t, and there’s lots of rules and lots of structure. Now that [life is] more free-floating, there’s anxiety.”
That’s perhaps why, for many students, mental health issues creep up for the first time when they start college. (The average age of onset for many mental health issues, including depression and bipolar disorder, is the early 20s.)
Dana Hashmonay was a freshman at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York in 2014 when she began having anxiety attacks before every class and crew practice, focusing on uncertainties about the future and comparing herself to seemingly well-adjusted classmates. “At that point, I didn’t even know I had anxiety. I didn’t have a name for it. It was just me freaking out about everything, big or small,” she says. When she tried to make an appointment with the counseling center, she was put on a two-week waitlist. When she finally met with a therapist, she wasn’t able to set up a consistent weekly appointment because the center was overbooked. “I felt like they were more concerned with, ‘Let’s get you better and out of here,’” she says, “instead of listening to me. It wasn’t what I was looking for at all.”

Instead, she started meeting weekly with an off-campus therapist, who her parents helped find and pay for. She later took a leave of absence midway through her sophomore year to get additional help. Hashmonay thinks the university could have done more, but she notes that the school seemed to be facing a lack of resources as more students sought help. “I think I needed something that the university just wasn’t offering,” she says.
A spokesperson for Rensselaer says the university’s counseling center launched a triage model last year in an effort to eliminate long wait times caused by rising demand, assigning a clinician to provide same-day care to students presenting signs of distress and coordinate appropriate follow-up treatment based on the student’s needs.
Some students delay seeing a counselor because they question whether their situation is serious enough to warrant it. Emmanuel Mennesson says he was initially too proud to get help when he started to experience symptoms of anxiety and depression after arriving at McGill University in Montreal in 2013 with plans to study engineering. He became overwhelmed by the workload and felt lost in classes where he was one student out of hundreds, and began ignoring assignments and skipping classes. “I was totally ashamed of what happened. I didn’t want to let my parents down, so I retreated inward,” he says. During his second semester, he didn’t attend a single class, and he withdrew from school that April.
For many students, mental health struggles predated college, but are exacerbated by the pressures of college life. Albano says some of her patients assume their problems were specific to high school. Optimistic that they can leave their issues behind, they stop seeing a therapist or taking antidepressants. “They think that this high school was too big or too competitive and college is going to be different,” Albano says. But that’s often not the case. “If anxiety was there,” she says, “nothing changes with a high school diploma.”
Counselors point out that college students tend to have better access to mental health care than the average adult because counseling centers are close to where they live, and appointments are available at little to no cost. But without enough funding to meet the rising demand, many students are still left without the treatment they need, says Ben Locke, Penn State’s counseling director and head of the Center for Collegiate Mental Health.
The center’s 2016 report found that, on average, universities have increased resources devoted to rapid-access services — including walk-in appointments and crisis treatment for students demonstrating signs of distress — since 2010 in response to rising demand from students. But long-term treatment services, including recurring appointments and specialized counseling, decreased on average during that time period.
“That means that students will be able to get that first appointment when they’re in high distress, but they may not be able to get ongoing treatment after the fact,” Locke says. “And that is a problem.”
‘We’re busier than we’ve ever been’
In response to a growing demand for mental health help, some colleges have allocated more money for counseling programs and are experimenting with new ways of monitoring and treating students. More than 40% of college counseling centers hired more staff members during the 2015-16 school year, according to the most recent annual survey by the Association for University and College Counseling Center Directors.
“A lot of schools charge $68,000 a year,” says Dori Hutchinson, director of services at Boston University’s Center for Psychiatric Rehabilitation, referring to the cost of tuition and room and board at some of the most expensive private schools in the country. “We should be able to figure out how to attend to their whole personhood for that kind of money.”
At the University of Iowa, Counseling Director Barry Schreier increased his staff by nearly 50% during the 2017-18 academic year. Still, he says, even with the increase in counseling service offerings, they can’t keep up with the number of students coming in for help. There is typically a weeklong wait for appointments, which can reach two weeks by mid-semester. “We just added seven full-time staff and we’re busier than we’ve ever been. We’re seeing more students,” Schreier says. “But is there less wait for service? No.”
The university has embedded two counselors in dorms since 2016 and is considering adding more after freshmen said it was a helpful service they would not have sought out on their own. Schreier also added six questions about mental health to a freshman survey that the university sends out several weeks into the fall semester. The counseling center follows up with students who might need help based on their responses to questions about how they’d rate their stress level, whether they’ve previously struggled with mental health symptoms that negatively impacted their academics, and whether they’ve ever had symptoms of depression or anxiety. He says early intervention is a priority because mental health is the number one reason why students take formal leave from the university.
As colleges scramble to meet this demand, off-campus clinics are developing innovative, if expensive, treatment programs that offer a personalized support system and teach students to prioritize mental wellbeing in high-pressure academic settings. Dozens of programs now specialize in preparing high school students for college and college students for adulthood, pairing mental health treatment with life skills classes — offering a hint at the treatments that could be used on campus in the future.
When Spigner took a medical leave from the University of Richmond, she enrolled in College Re-Entry, a 14-week program in New York that costs $10,000 and aims to provide a bridge back to college for students who have withdrawn due to mental health issues. She learned note-taking and time management skills in between classes on healthy cooking and fitness, as well as sessions of yoga and meditation.
Mennesson, the former McGill engineering student, is now studying at Westchester Community College in New York with the goal of becoming a math teacher. During his leave from school, he enrolled in a program called Onward Transitions in Portland, Maine that promises to “get 18- to 20-somethings unstuck and living independently” at a cost of over $20,000 for three months, where he learned to manage his anxiety and depression.
Another treatment model can be found at CUCARD in Manhattan, where patients in their teens and early 20s can slip on a virtual reality headset and come face-to-face with a variety of anxiety-inducing simulations — from a professor unwilling to budge on a deadline to a roommate who has littered their dorm room with stacks of empty pizza boxes and piles of dirty clothes. Virtual reality takes the common treatment of exposure therapy a step further by allowing patients to interact with realistic situations and overcome their anxiety. The center charges $150 per group-therapy session for students who enroll in the four-to-six-week college readiness program but hopes to make the virtual reality simulations available in campus counseling centers or on students’ cell phones in the future.
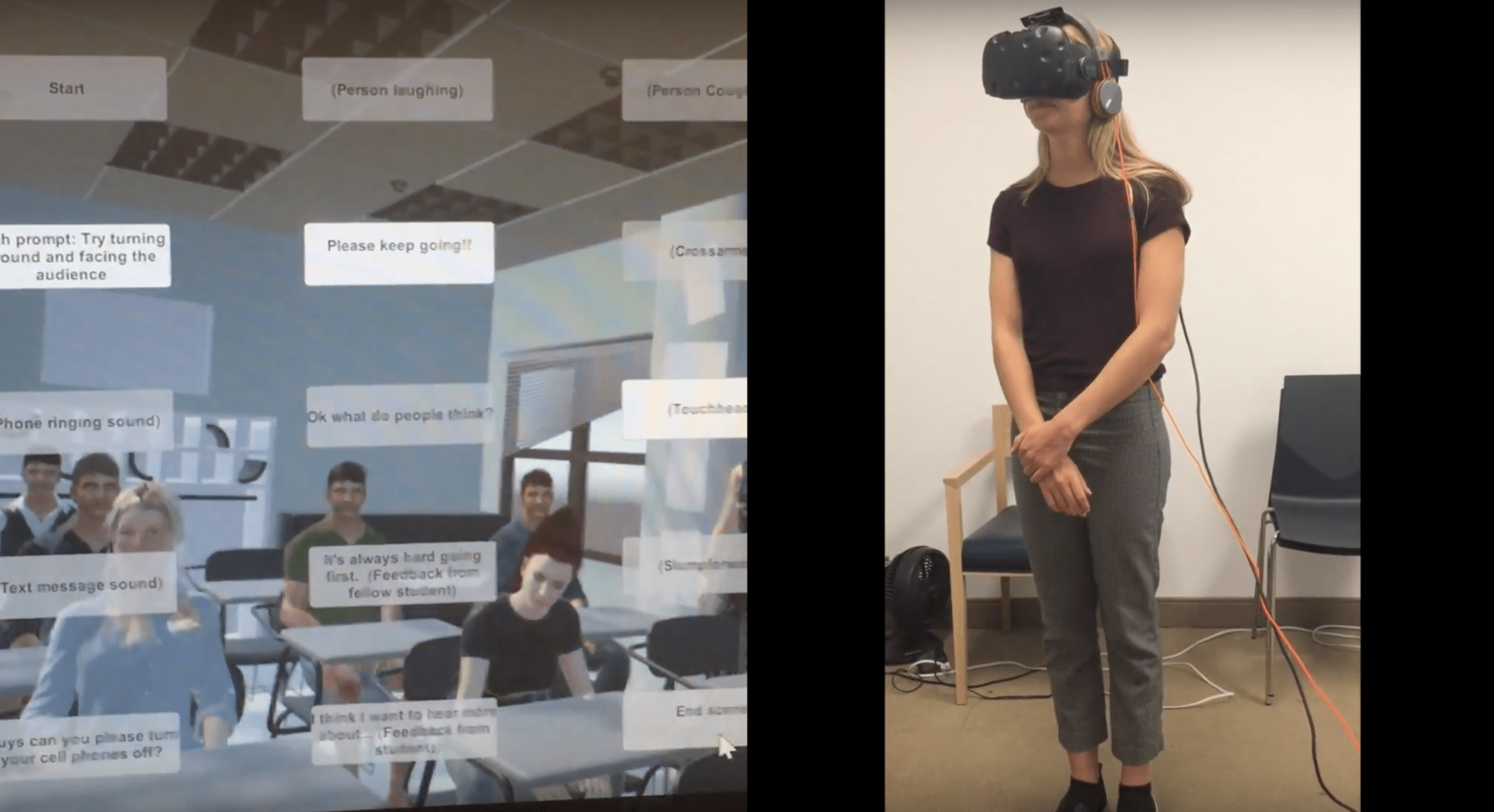
Hashmonay, who has used the virtual reality software at the center, says the scenarios can be challenging to confront, “but the minute it’s over, it’s like, ‘Wow, OK, I can handle this.’” She still goes weekly to therapy at CUCARD, and she briefly enrolled in a Spanish course at Montclair State University in New Jersey in January. But she withdrew after a few classes, deciding to get a job and focus on her health instead of forcing a return to school before she is ready. “I’m trying to live life right now and see where it takes me,” she says.
Back at the University of Richmond for her senior year, Spigner says the attitude toward mental health on campus seems to have changed dramatically since she was a freshman. Back then, she knew no one else in therapy, but most of her friends now regularly visit the counseling center, which has boosted outreach efforts, started offering group therapy and mindfulness sessions, and moved into a more private space. “It’s not weird to hear someone say, ‘I’m going to a counseling appointment,’ anymore,” she says.
She attended an open mic event on Richmond’s campus earlier this semester, where students publicly shared stories and advice about their struggles with mental health. Spigner, who meets weekly with a counselor on campus, has become a resource to many of her friends because she openly discusses her own mental health, encouraging others not to be ashamed to get help.
“I’m kind of the go-to now for it, to be honest,” she says. “They’ll ask me, ‘Do you think I should go see counseling?’” Her answer is always yes.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Donald Trump Is TIME's 2024 Person of the Year
- Why We Chose Trump as Person of the Year
- Is Intermittent Fasting Good or Bad for You?
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- The 20 Best Christmas TV Episodes
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Write to Katie Reilly at Katie.Reilly@time.com