On July 16, 1945, the Atomic Age was born when a device with an explosive “yield” roughly equal to 20 kilotons of TNT was detonated in the desert of southeastern New Mexico. The explosion was so inconceivably violent, so fearsome, that one witness to the event, the physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer, famously claimed that a line from the Bhagavad Gita, a Hindu scripture, ran unbidden through his head: “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds.”
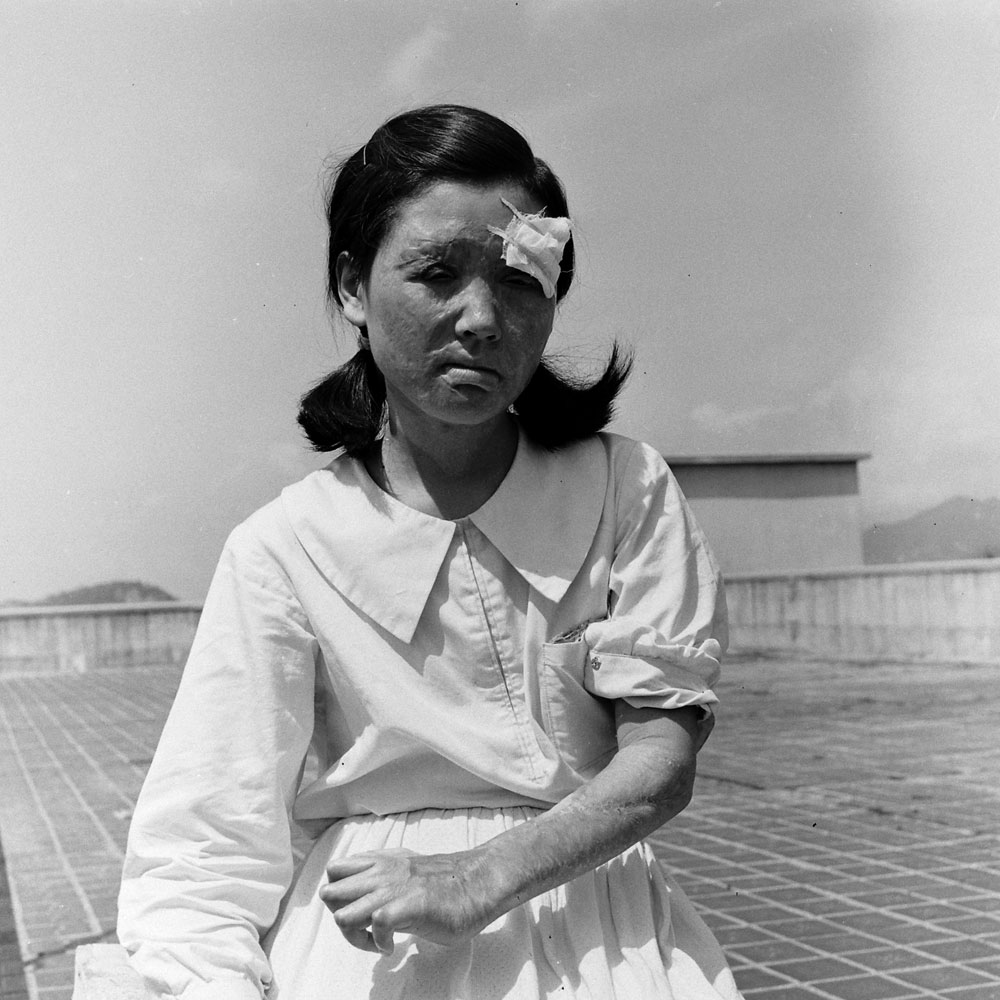
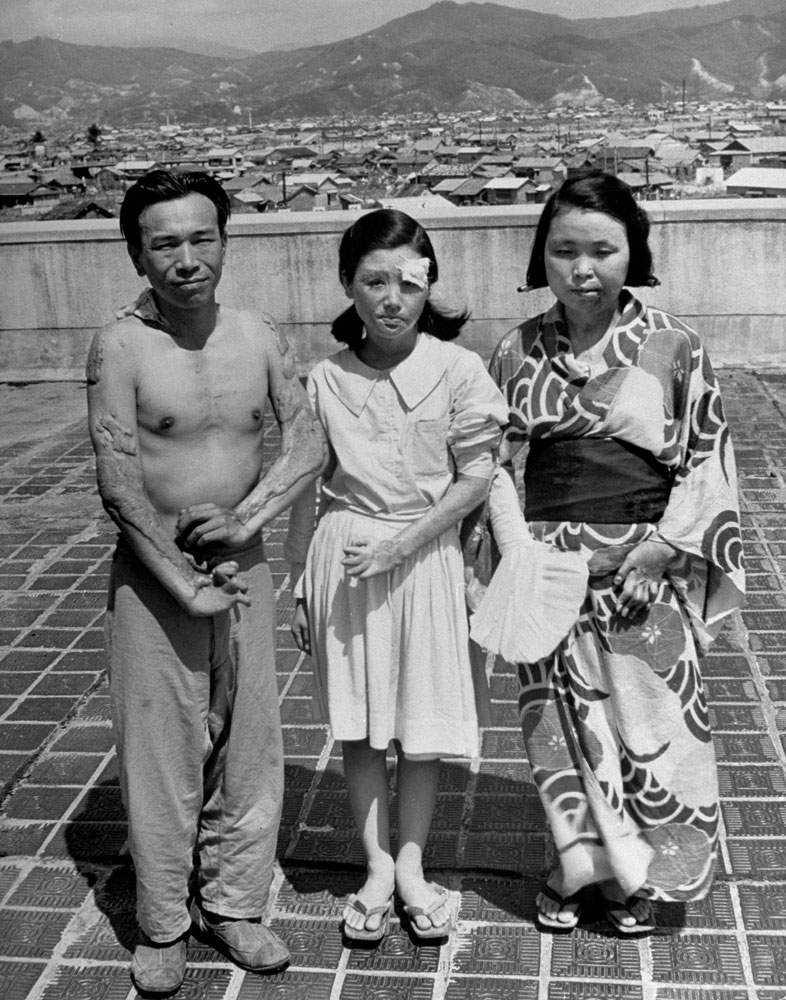
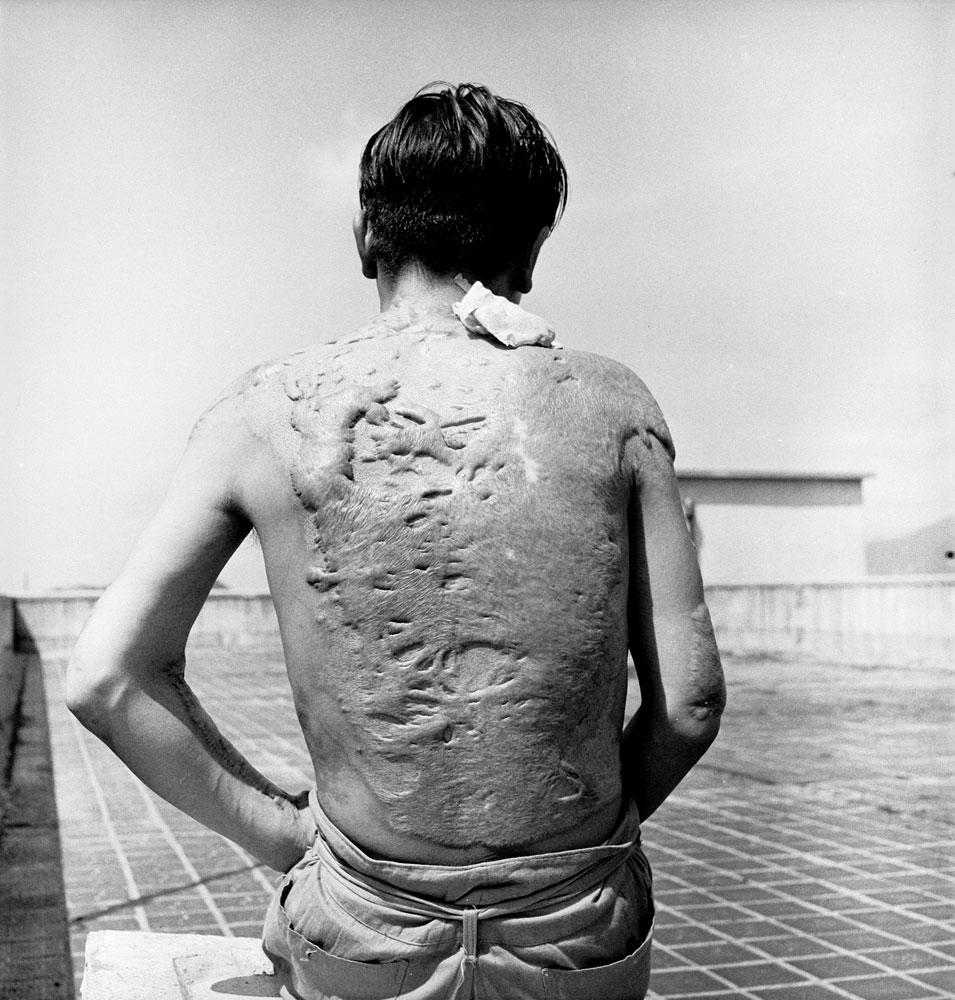
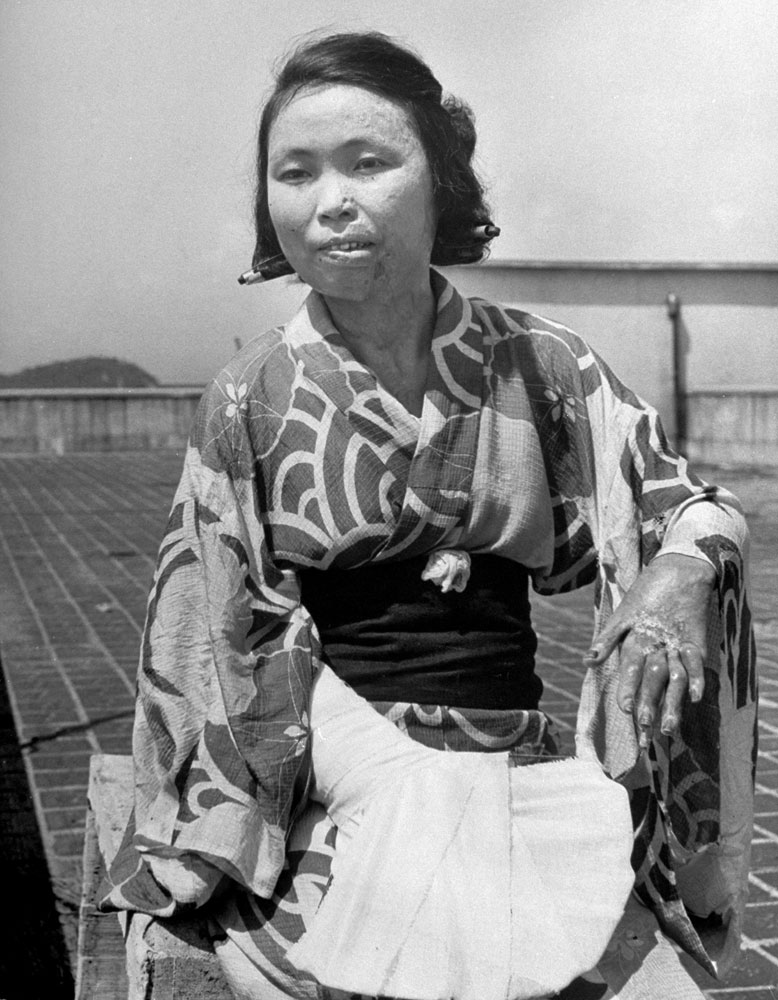
Less than a month later, American forces dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing tens of thousands of men, women and children in an instant; condemning thousands more to slow, agonizing deaths from burns and radiation sickness in the months and years to come; and, in the eyes of most historians, both Western and Asian, hastening the surrender of the Japanese and bringing about the end of the Second World War.
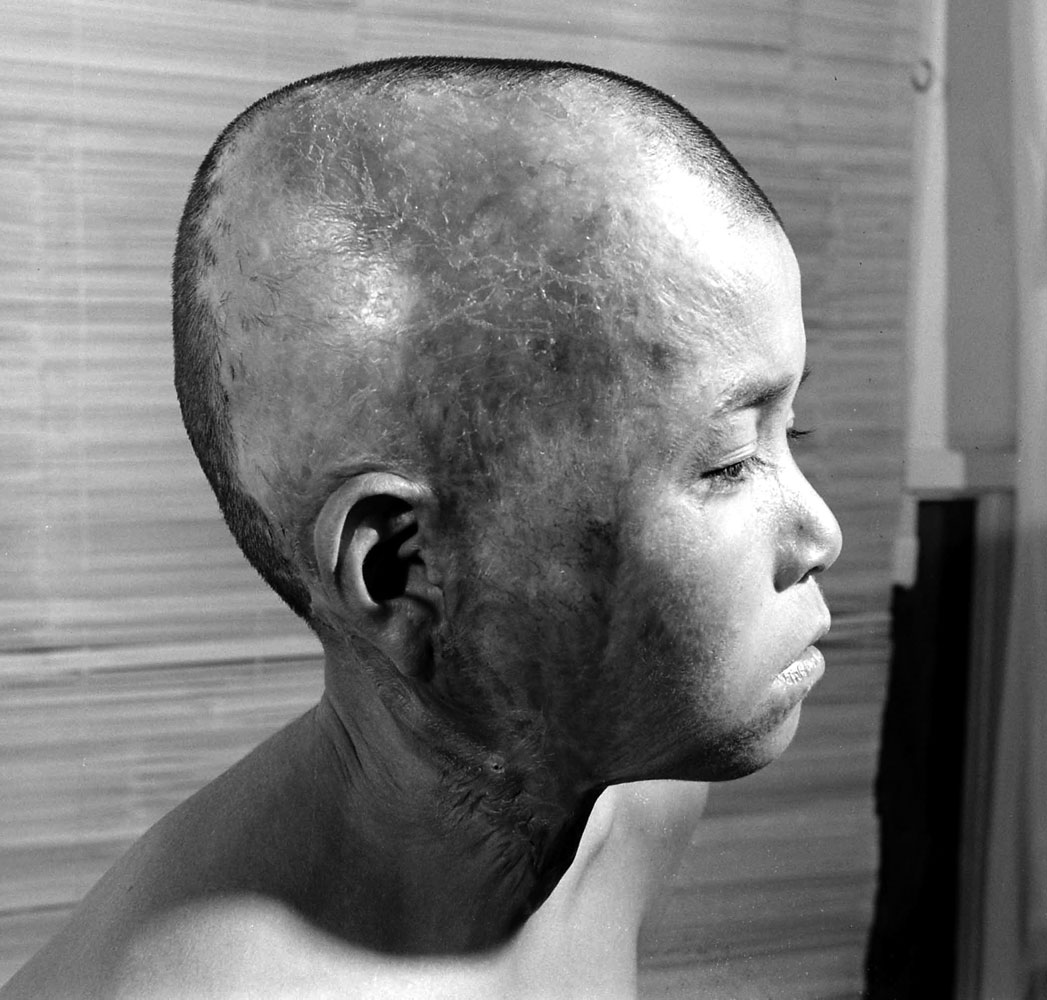
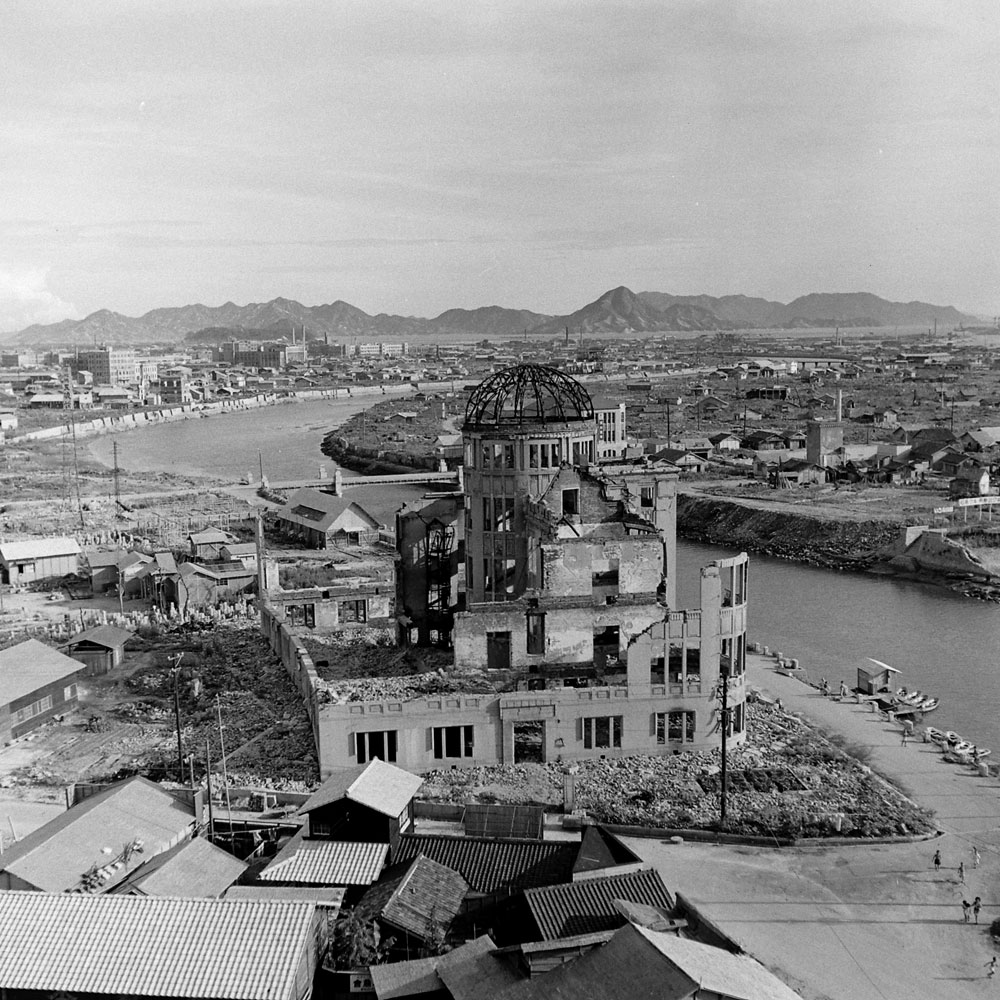
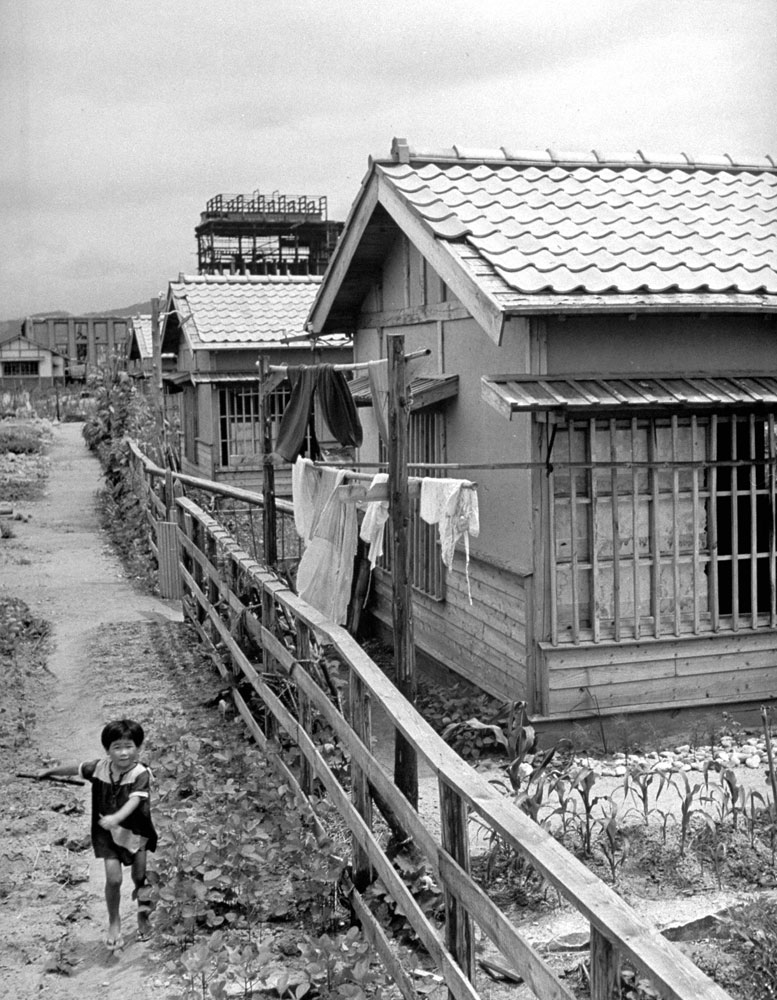
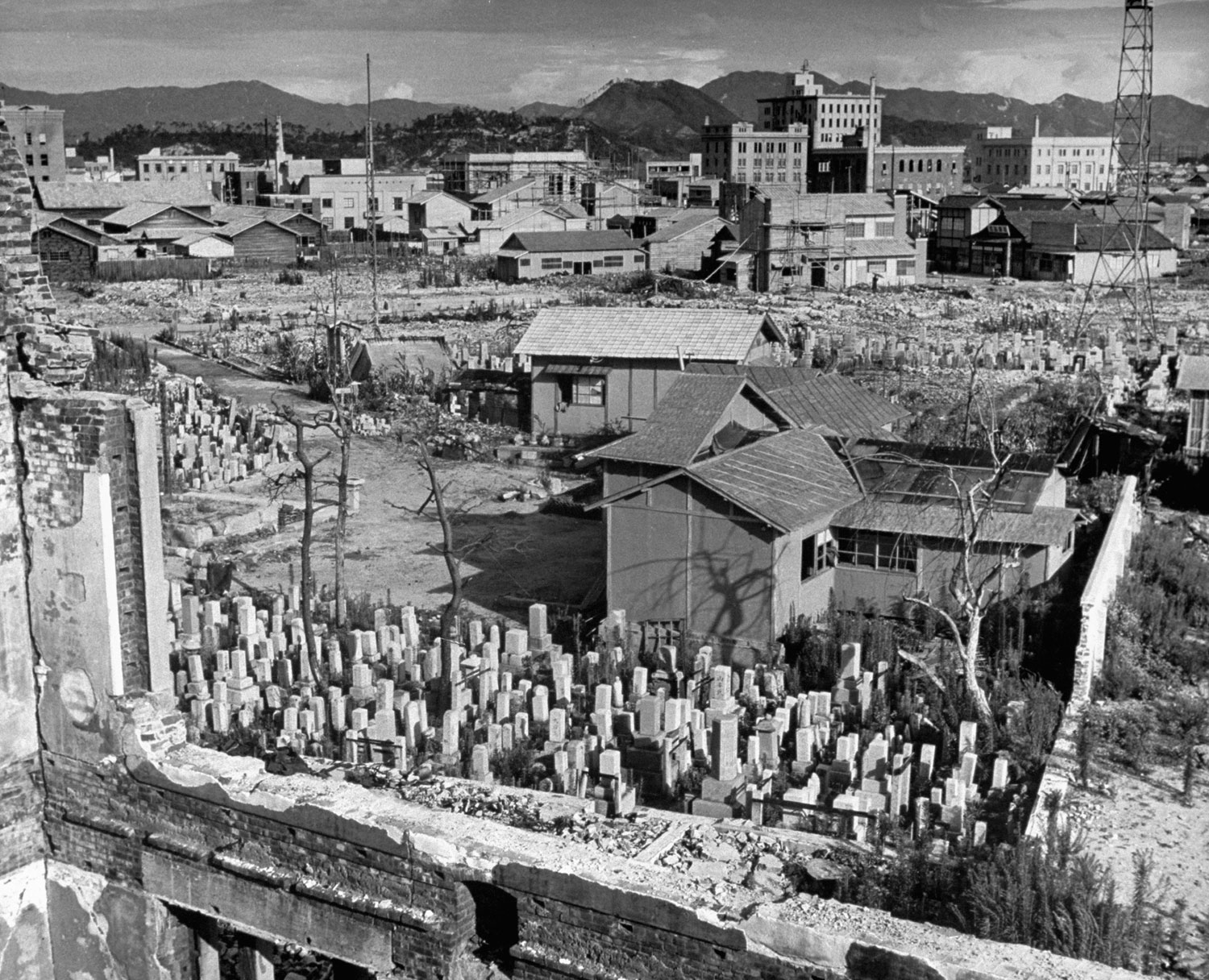
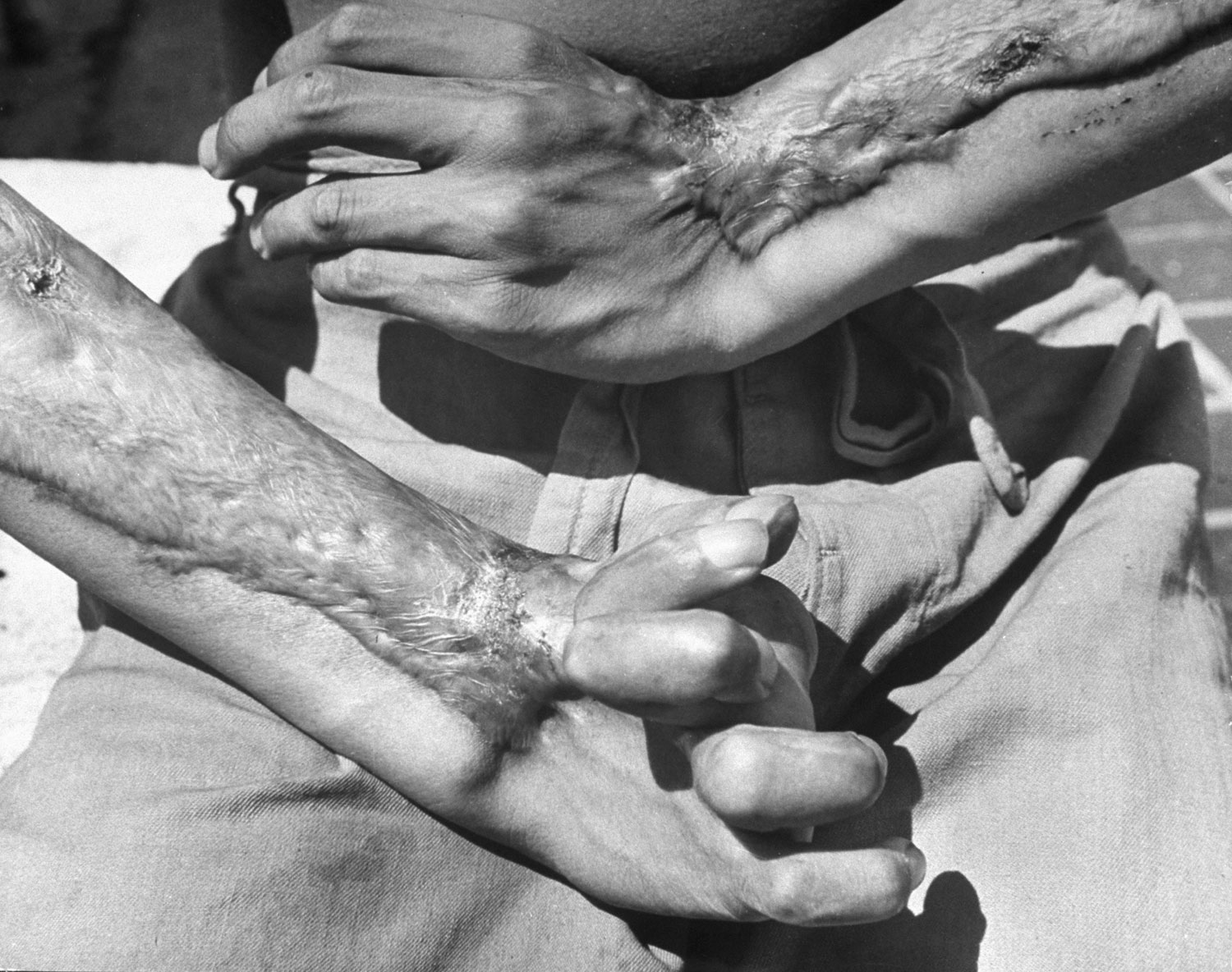
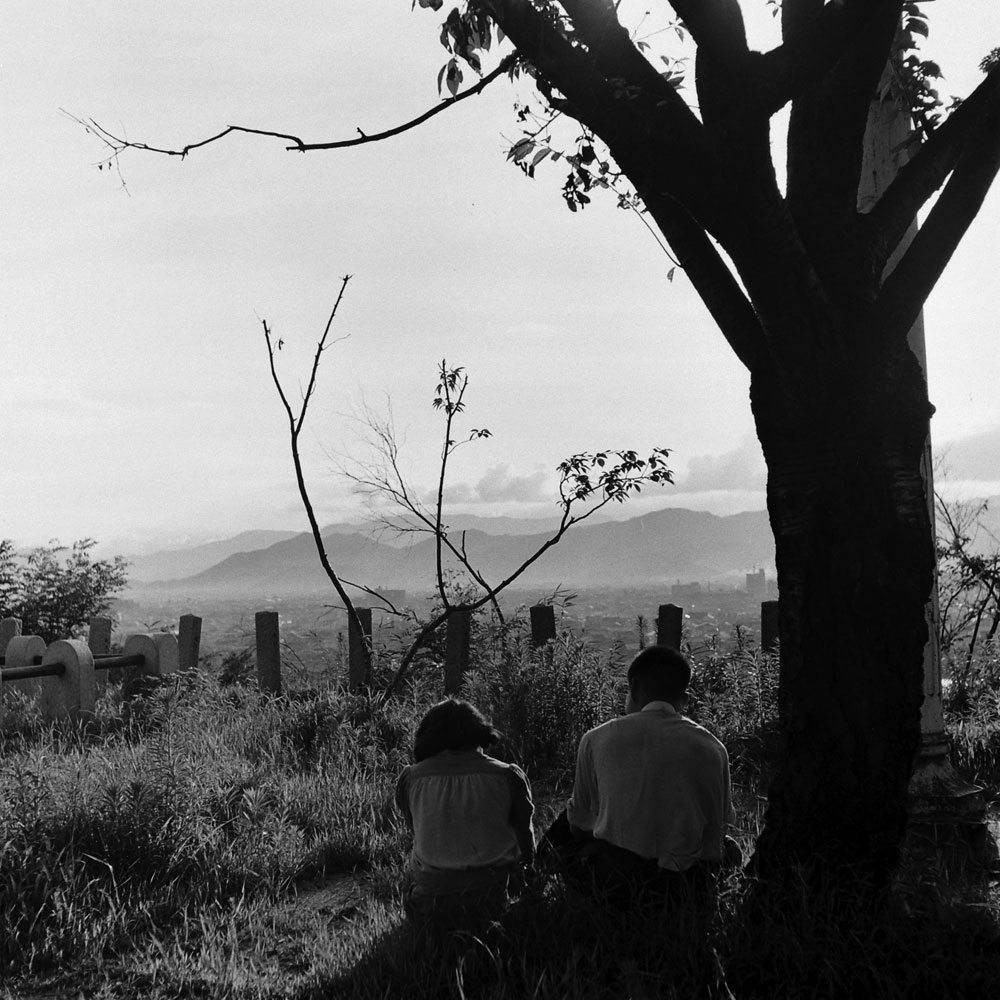
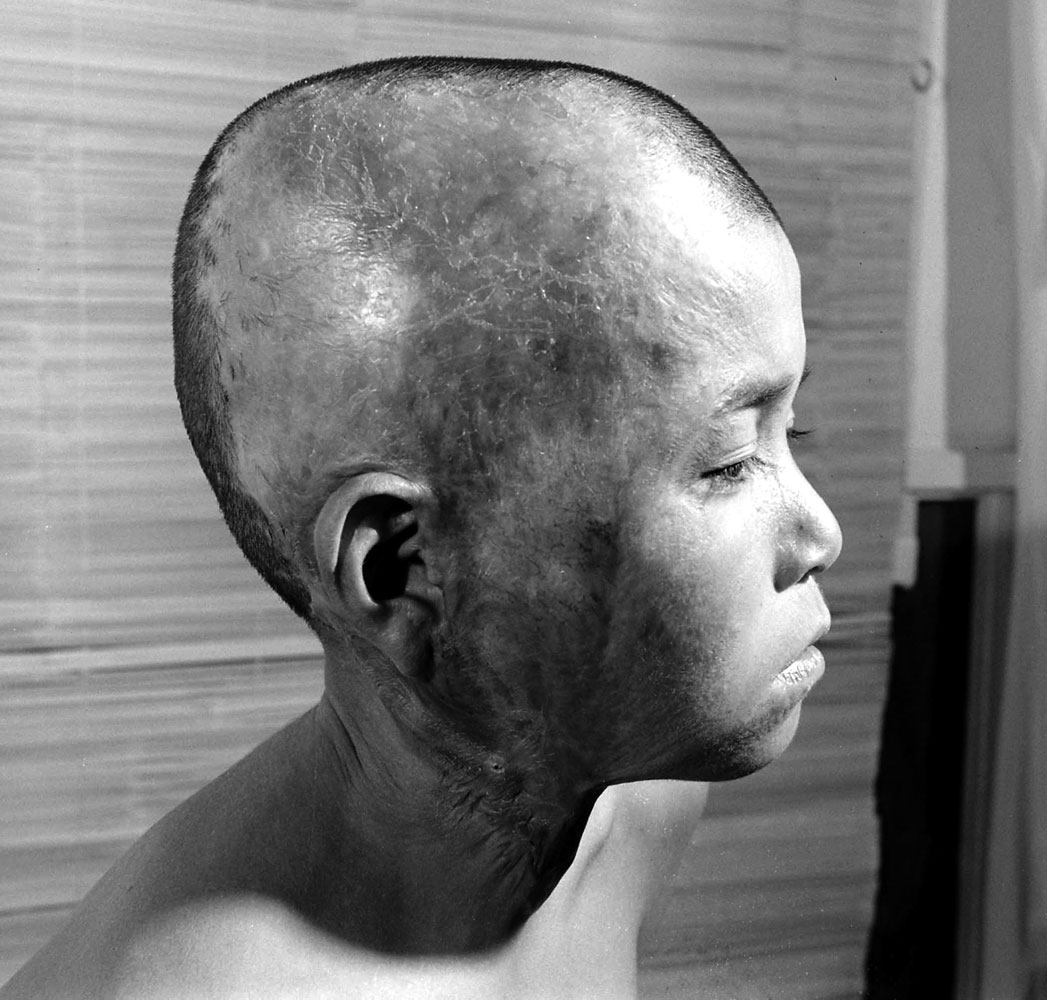
Here, LIFE.com presents a selection of photographs, most of which were never published in LIFE magazine, taken in Hiroshima after the war ended. In the landscape of a ruined city, and on the scarred skin and misshapen limbs of Japanese who survived the world’s first nuclear attack, photographer Carl Mydans discovered the legacy — part nightmare, part surprising, wishful dream — of those world-changing explosions.
As LIFE put it to the magazine’s readers in September 1947:
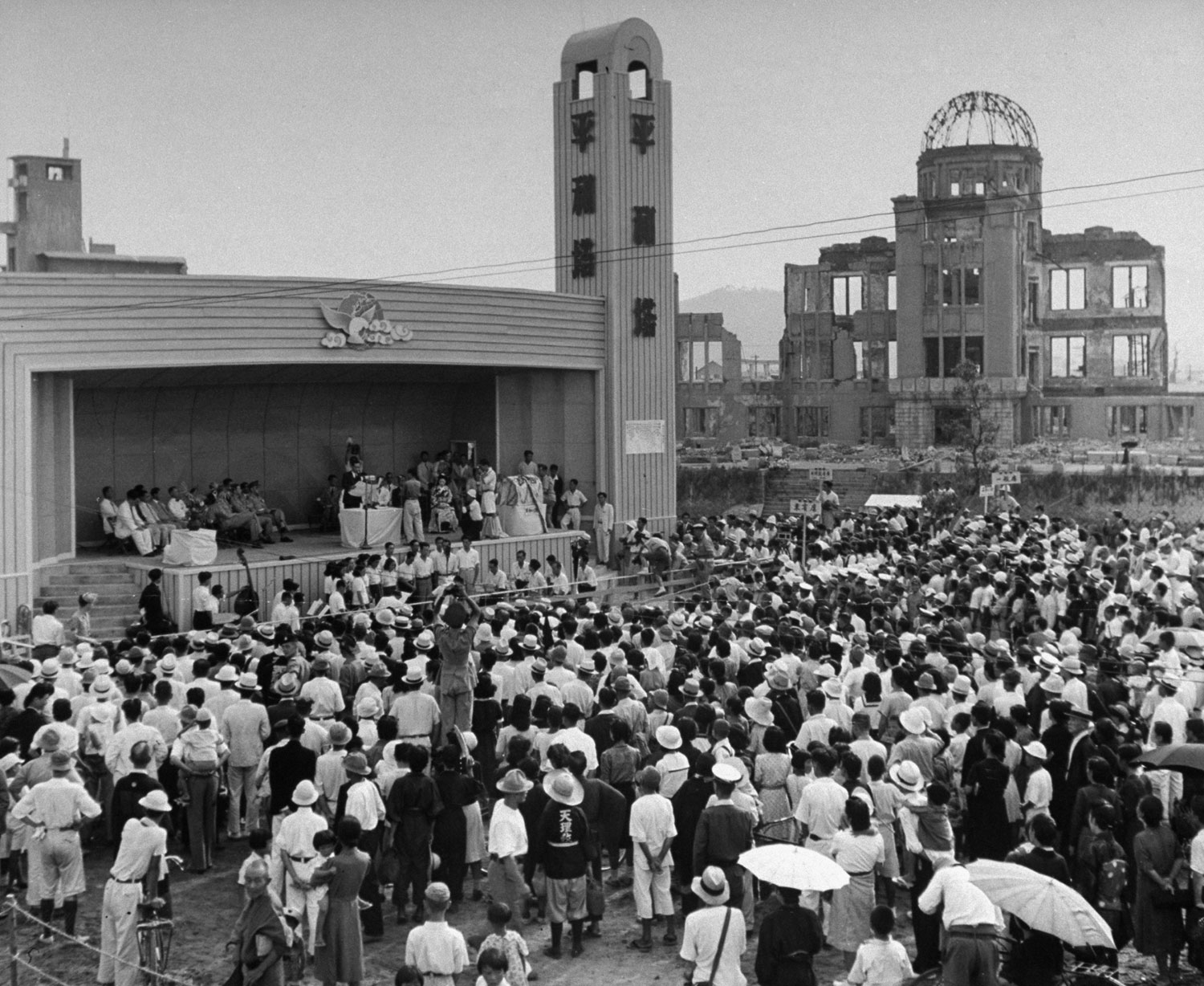
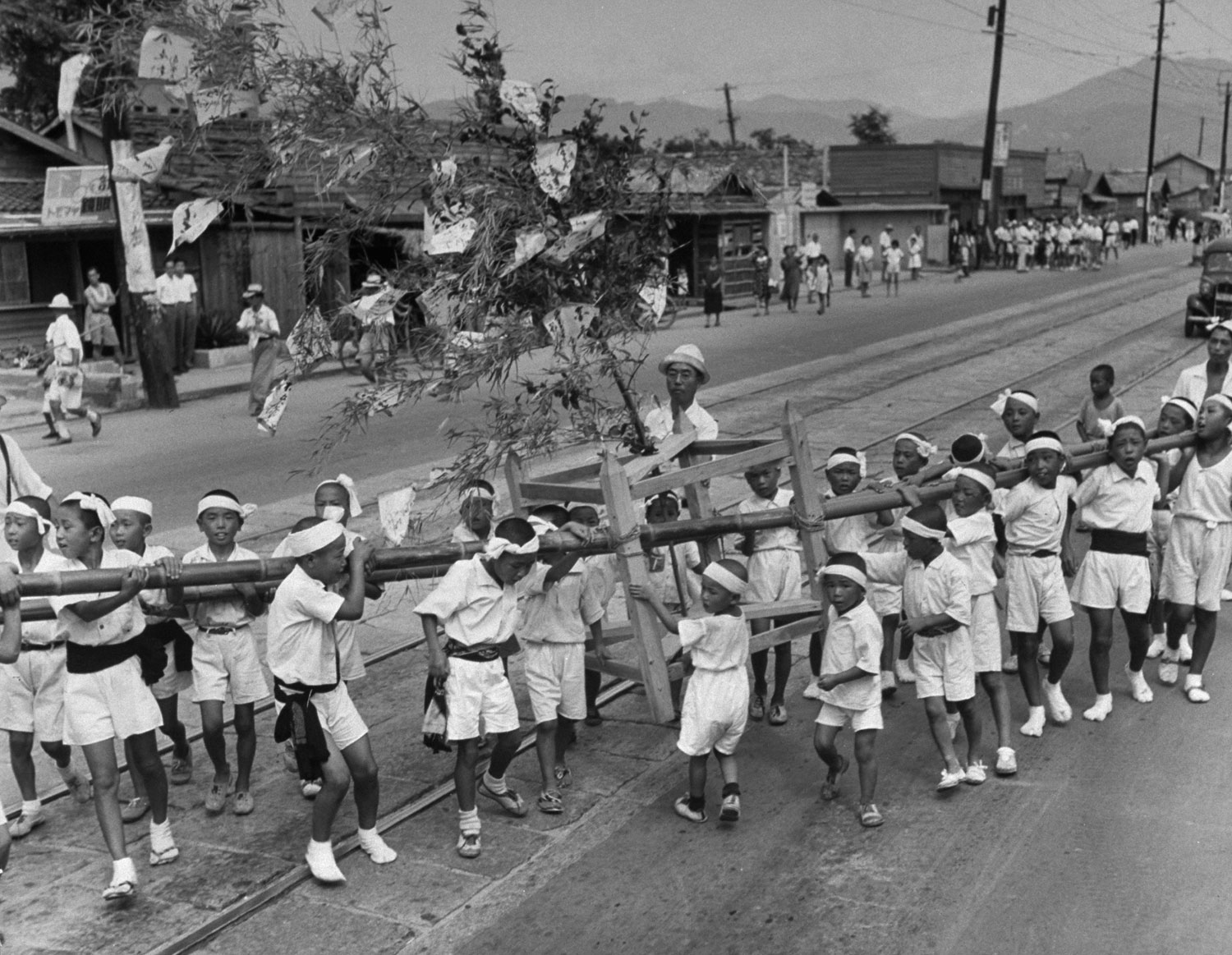
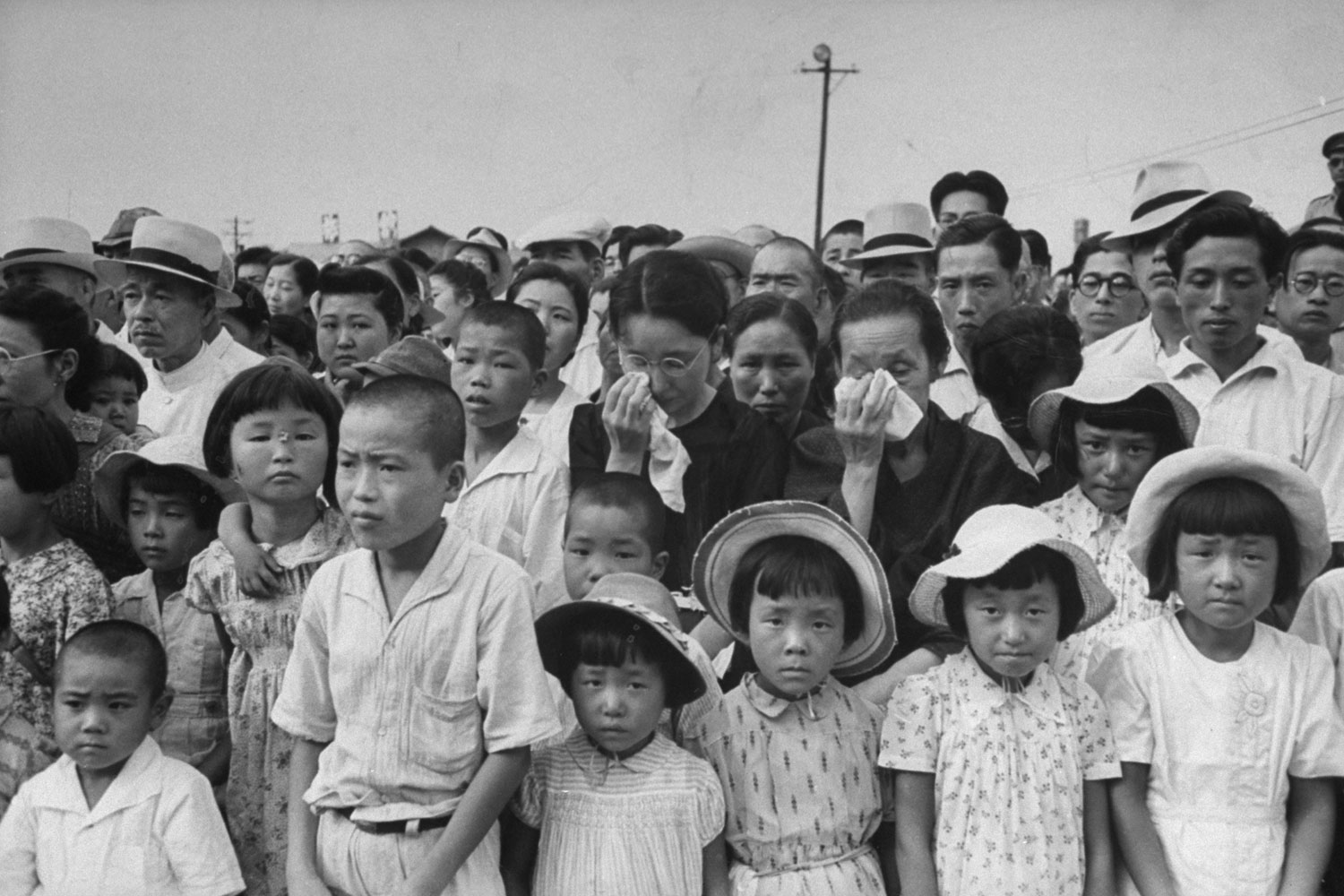
On August 6, two years to the day and the minute after the first atomic bomb devastated their city, the people of Hiroshima, Japan, gathered to mourn — but, more surprising, to celebrate as well. A startled world read that Hiroshima, proclaiming itself the new world mecca for peace, had held a carnival. The people planted camphor tree, which is a symbol for long life, and they prayed, too. But then they paraded through the streets, listened to speeches and had fun. Hiroshima seemed to have risen from the dead. The people were putting their city back on the map. The spirit was that of a U.S. boom town in the late 1800s. Their motto: Look at us and forego war.
The only civilian correspondent covering the ceremonies, LIFE’s Carl Mydans, questioned the people and took pictures. He found that Hiroshima had made tremendous strides in recovery. A population reduced from 250,000 to 175,000 in one blinding flash had slowly grown back to 210,000. Of 60,000 houses destroyed 23,000 have been rebuilt. Stores with Western names have opened shop. There is a drive on to get tourist trade and a movement to package and export bits of fused rubble to the rest of the world.
The booster spirit of resurgent Hiroshima would warm the heart of any Rotarian. The imponderables in the phenomenon might baffle a philosopher. It was easy for cynical “experts” to note the traditional Japanese love of novelty, their commercialism and their ability to be led, either for good or evil. But then, no atomic bombs have fallen on the “experts.” Like other men who have watched postwar Hiroshima, Lieut. Colonel Thomas Cloward, chief of American Military Government stationed there, could only say, “We don’t know what is the truly motivating force. All we know is that something’s happened to these people. They want peace, and they want to play a part in that peace.”











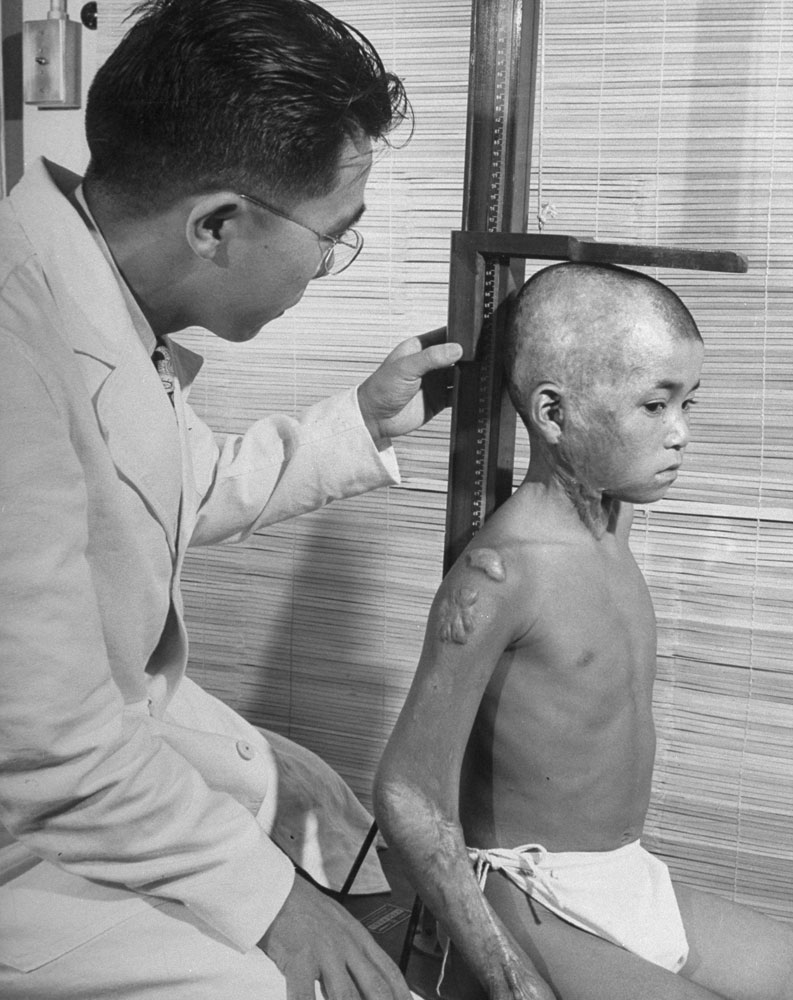
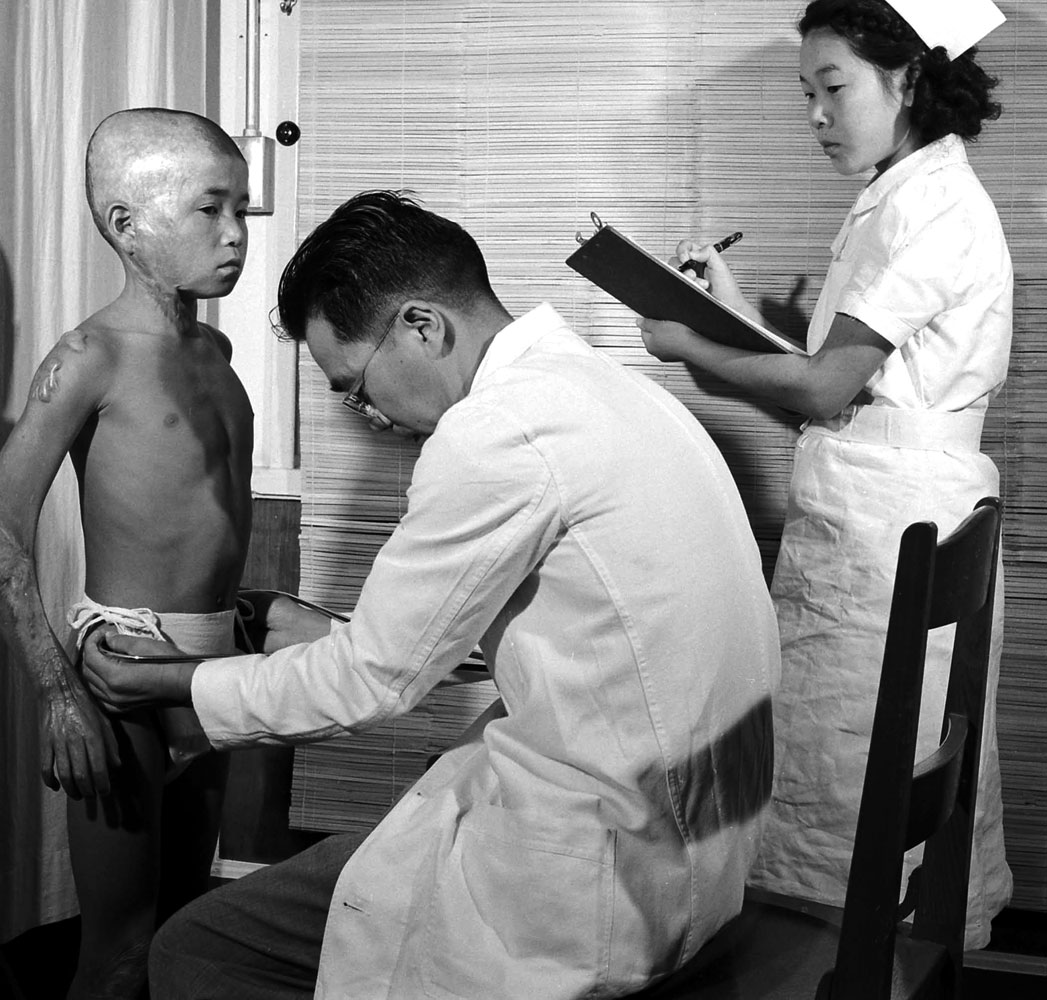
![Hiroshima's children patiently wait their turn for a complete and detailed physical examination in ABCC's [Atom Bomb Casualty Commission] temporary laboratory clinic.](https://api.time.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/14_00717439.jpg?quality=75&w=2400)


More Must-Reads from TIME
- Donald Trump Is TIME's 2024 Person of the Year
- Why We Chose Trump as Person of the Year
- Is Intermittent Fasting Good or Bad for You?
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- The 20 Best Christmas TV Episodes
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Contact us at letters@time.com