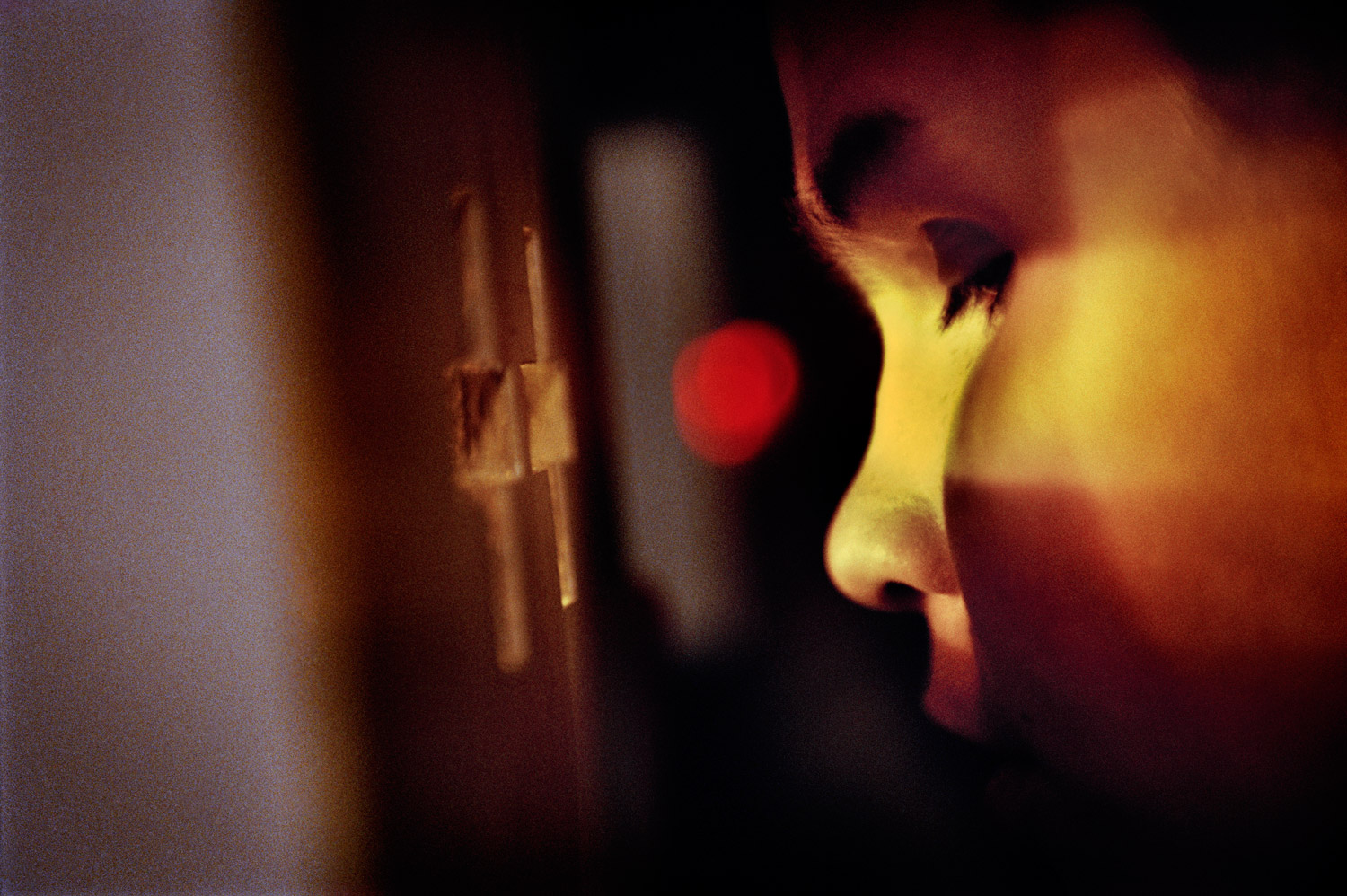
For the first time ever, World Press Photo is awarding multimedia in its annual competition. In March, the jury, chaired by photographer Ed Kashi, announced six finalists in two categories: linear and interactive. Among them is a ground breaking production entitled Blanco, a project exploring blindness across the globe by Italian photographer Stefano De Luigi.
Through a mesmerizing series of fades and transitions, pans and movements, the photographs appear to come alive. Backgrounds blur, move slightly, then disappear into white. De Luigi’s images, which is also a book and exhibition, depict the affect and treatment of blindness in 14 countries – from schools for the blind in Bulgaria and India, to diagnosis and treatment in Vietnam and China.
To create Blanco, De Luigi approached RAT Creatives, a multimedia design studio in Rome, proposing they create a piece to accompany the exhibition. Annalisa D’Angelo, a director at RAT Creatives, said the inspiration for the production, which she refers to as “e-motion” as opposed to “multimedia”, was Fernando Meirelles’s film, “Blindness.”
“Stefano had given us a fundamental keyword we kept in mind throughout the whole process: ‘white’” she said. “Before starting the actual video we made a precise storyboard we proposed to Stefano. He accepted it and the work started.”
A composer, Simonluca Laitempergher, created the original score while watching the nearly-completed film. D’Angelo said the ring tone heard throughout the piece is a reference to Meirelles’s film, “This sound, almost pure, is the musical correspondent of white. It has an organizational function both from a dramaturgical point of view and a symbolic one,” she said. ”It is a reference to purity. “
De Luigi said working on Blanco was a unique experience, adding, “What I am most happy about is that Annalisa and Ippolito, the directors of Blanco, have deeply understood what drove me all these years working on blindness.”
The winners will be announced May 7 at the World Press Photo awards ceremony in Amsterdam.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Why Maternity Care Is Underpaid
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at letters@time.com