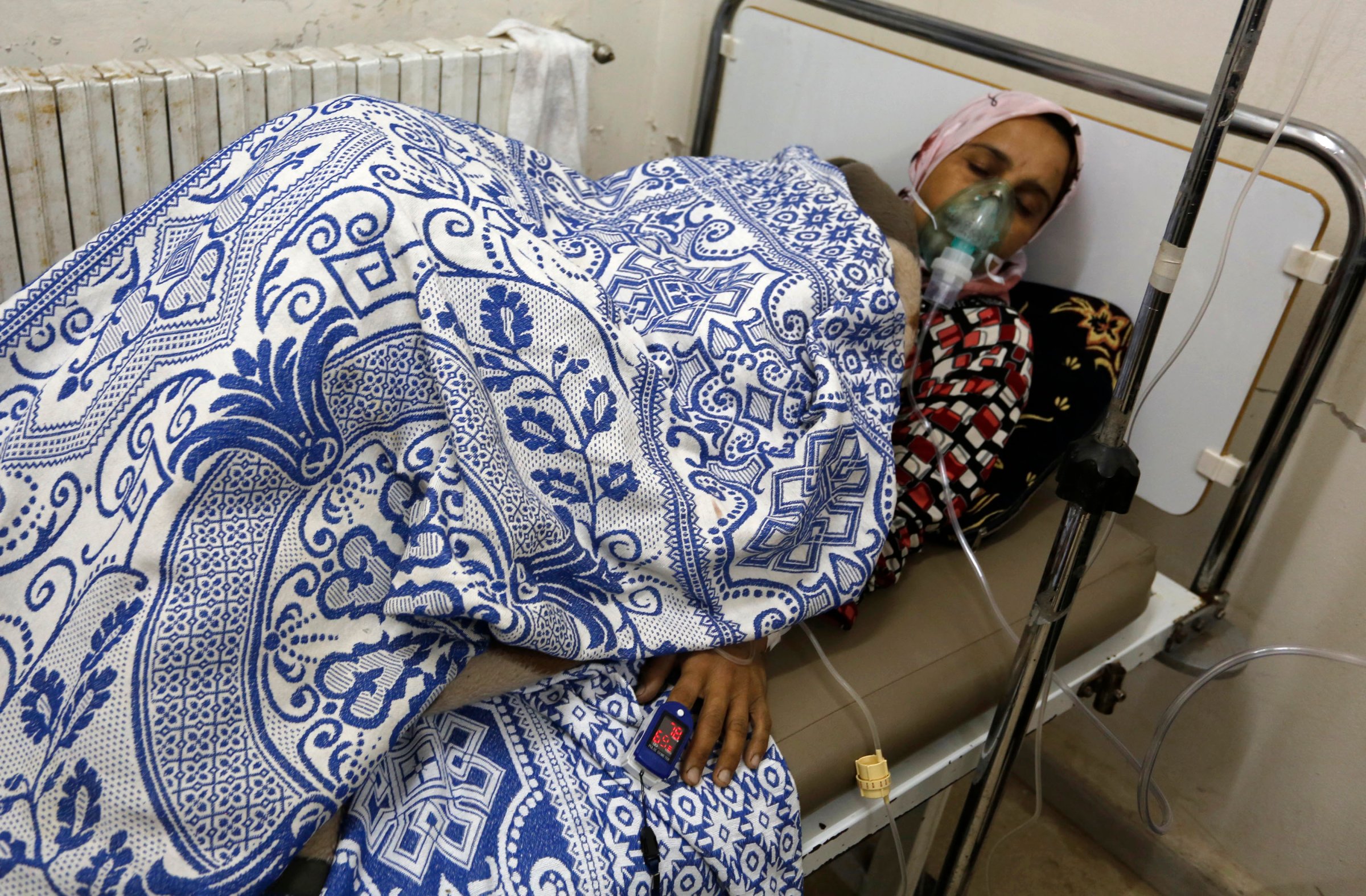
A team of researchers at the University of Tennessee at Knoxville has identified an enzyme produced in the bodies of squid that may be effective in breaking down nerve gasses and other deadly chemical weapons.
The team’s study, recently published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry, focused on engineering the improvement of these proteins — known as “bioscavengers” — that “chew up” nerve agents like sarin, a chemical infamous for its use as a weapon in the ongoing Syrian civil war and in a terrorist attack on the Tokyo subway in 1995.
The team aspires to create a prophylactic drug from these enzymes that will mitigate their harmful effects on humans, but first they must modify the enzymes to ensure that the human body won’t destroy them first.
“Using an enzyme from a squid as a bioscavenger in humans is problematic because the human body will recognize it as a foreign substance and chop it up,” said research team member Jerry Parks, adding that “other groups have already shown possible ways to get around that problem.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Donald Trump Is TIME's 2024 Person of the Year
- Why We Chose Trump as Person of the Year
- Is Intermittent Fasting Good or Bad for You?
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- The 20 Best Christmas TV Episodes
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Contact us at letters@time.com