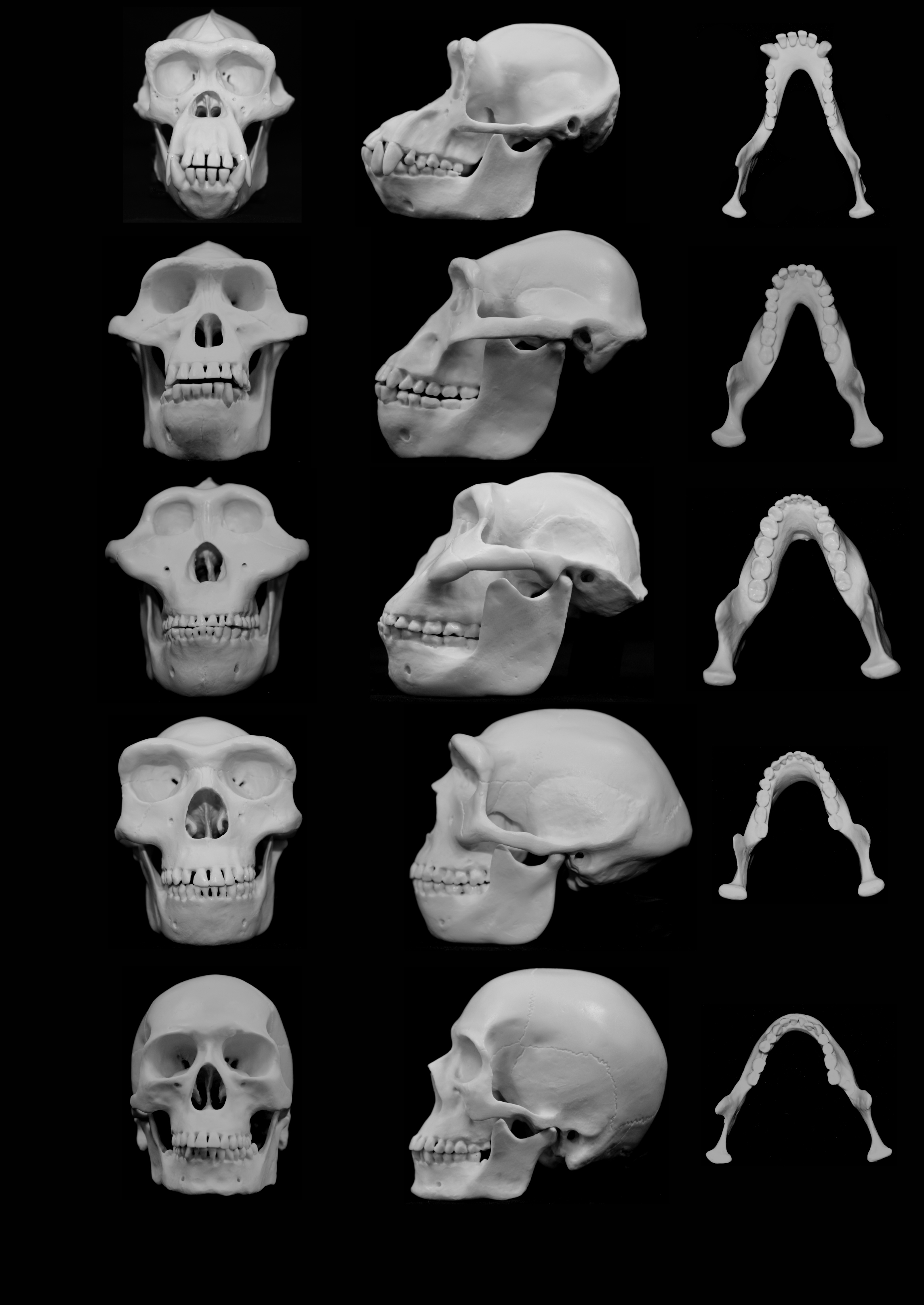
Humans evolved to minimize injury incurred by punches to the face, a new study suggests.
Researchers at the University of Utah observed that the fossils of australopiths—bi-peds that lived 4-5 million years ago and directly preceded the human genus Homo—had robust cheek, jaw, eye and nose features. Scientists had previously thought that the australopiths’ strong facial features were an evolutionary adaptation to their hardy diet, but the study published in the journal Biological Reviews suggests that they were likely eating softer foods like fruit.
Dr. David Carrier, the lead researcher in the study, told the Guardian that the australopiths’ hands had adapted to form a fist, allowing them to engage in hand-to-hand combat. “When modern humans fight hand to hand, the face is usually the primary target,” Carrier said. Carrier and his team found that the bones that had evolved to be more robust were typically the features that suffer the greatest impact in a fight.
The study also shows that while the faces, hands and up-right nature of australopiths evolved to allow for improved fighting, modern-day humans have less robust facial features. Carrier told BBC that humans have less of a need to protect themselves because violence is no longer a driving evolutionary factor. “There’s a temporal correlation,” Carrier said.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Why Biden Dropped Out
- Ukraine’s Plan to Survive Trump
- The Rise of a New Kind of Parenting Guru
- The Chaos and Commotion of the RNC in Photos
- Why We All Have a Stake in Twisters’ Success
- 8 Eating Habits That Actually Improve Your Sleep
- Welcome to the Noah Lyles Olympics
- Get Our Paris Olympics Newsletter in Your Inbox
Contact us at letters@time.com