
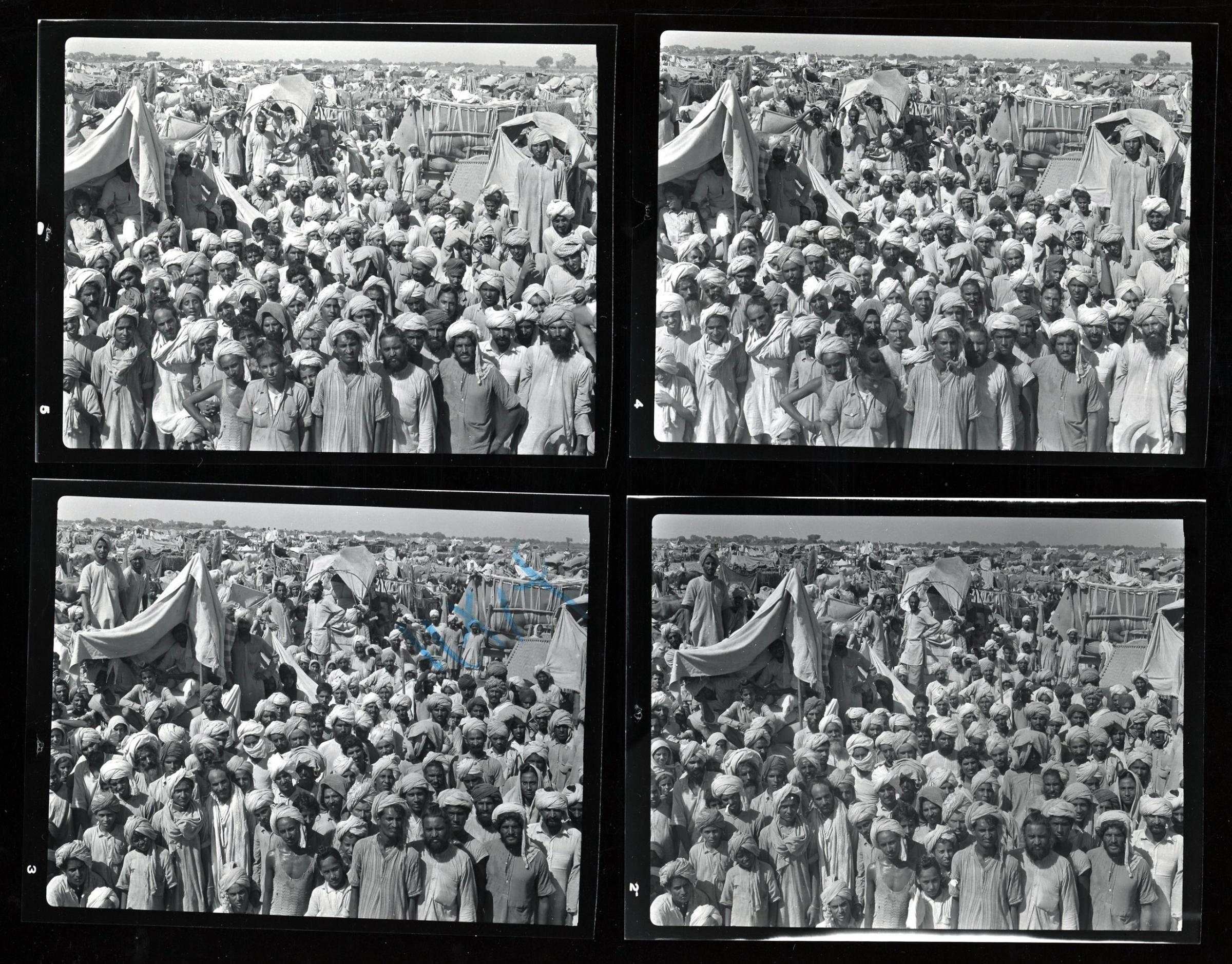
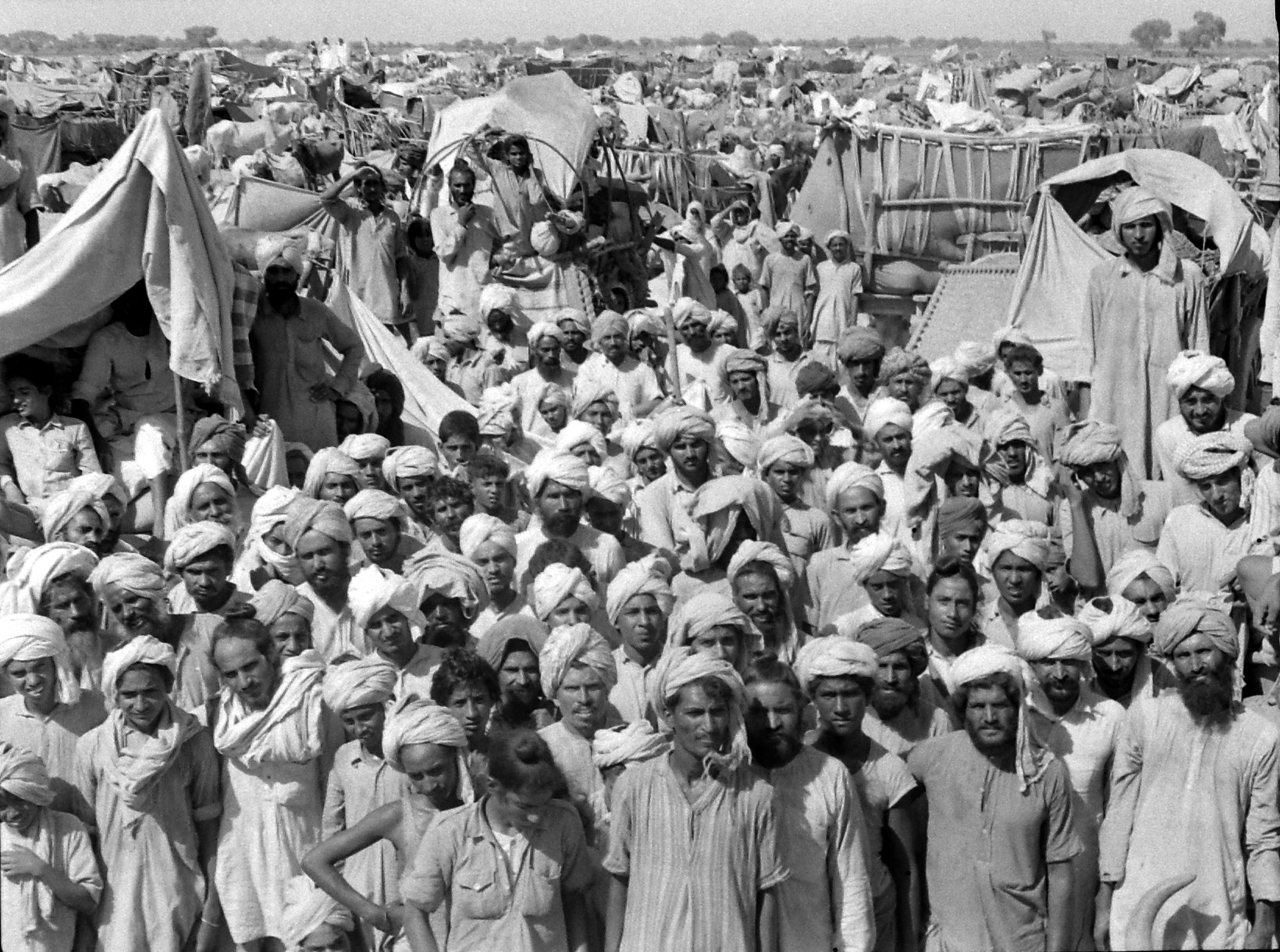
The migration that accompanied India’s independence and partition in 1947 was the largest movement of peoples in human history, but almost no one expected it to happen. When the new Muslim homeland of Pakistan split off from the former British Indian empire, it was accepted that people might shift across the new borders, but India’s religious communities were so intertwined that mass transfers of population seemed impossible. In the event, around 16 million Hindus, Sikhs and Muslims were driven out by reciprocal pogroms, and became a modern phenomenon: migrants.
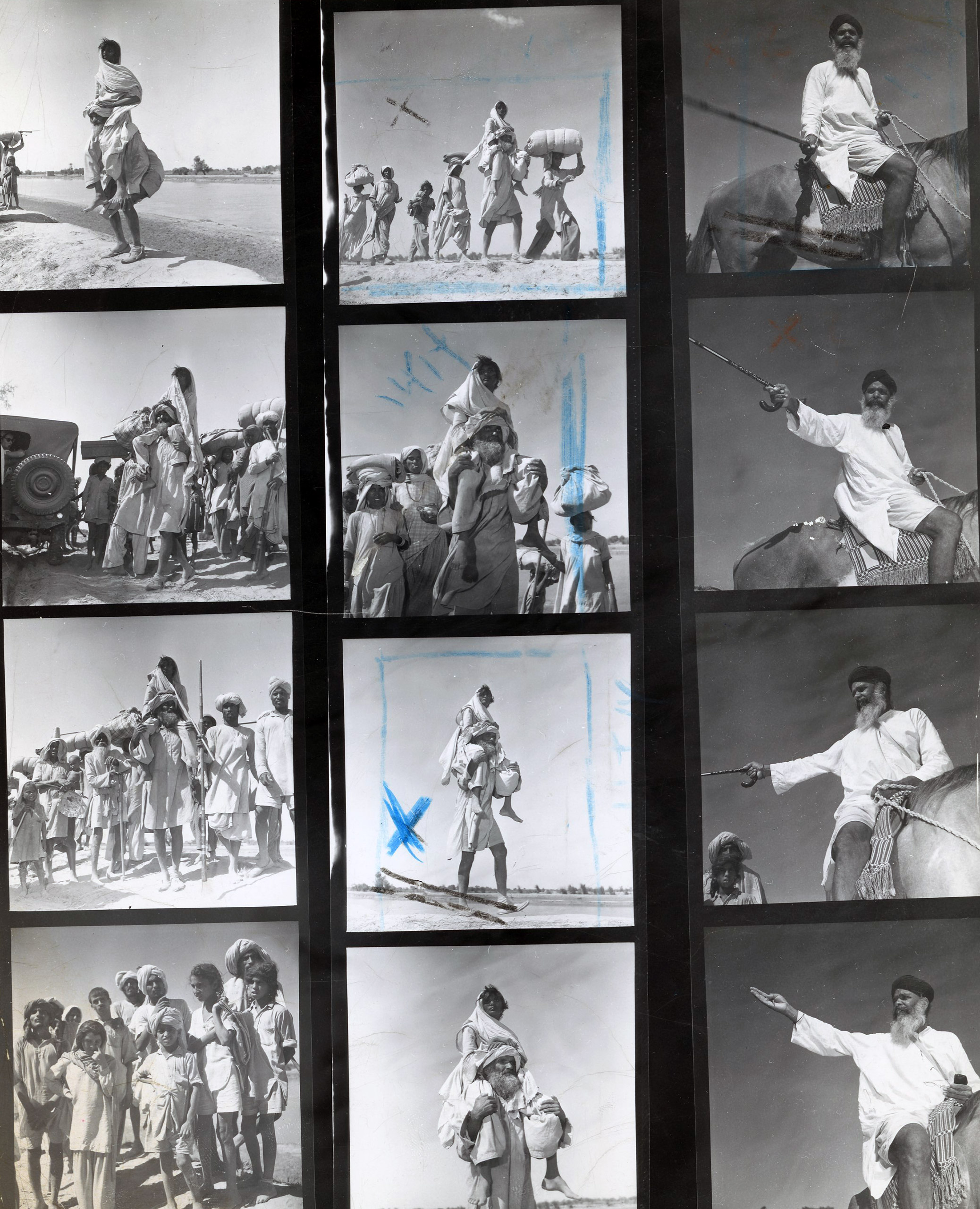
Surprisingly few photographs of this world-changing exodus survive, and some of the best were taken by Margaret Bourke-White for LIFE. The rediscovery of her contact sheets, together with the notes written by the reporter Lee Eitingon, give a powerful sense of how she did it. Having chronicled the liberation of Buchenwald and nearly every theatre of war in World War II, the celebrated and notoriously resourceful Bourke-White was not fazed by the chaos of a newly divided subcontinent. Eitingon, though in her mid-20s, was an experienced conflict reporter. A note in the archives reads: “Old India hands warned that the assignment was impossible for women – transportation would be difficult, native women were being abducted, even British army officers were being attacked.”

Ingeniously, they obtained a Jeep and an escort of a few soldiers from the military authorities—including an English captain nicknamed ‘Snuggles’—and drove to Punjab. “We were dressed in khaki shirts and slacks,” Eitingon wrote, “and we carried bedrolls, a four-gallon thermos of purified water, camera equipment and typewriter.” Although they were certainly aided by Bourke-White privilege, the two women were constantly close to danger. Driving towards Lahore, they encountered a stalled truck packed with refugees, which was in the process of being surrounded “by about 30 men with ten-foot-long spears.” The soldiers in their escort intervened. “The captain shot one attacker, then leaped into the Jeep. A stray shot followed us as we drove off,” wrote Eitingon.
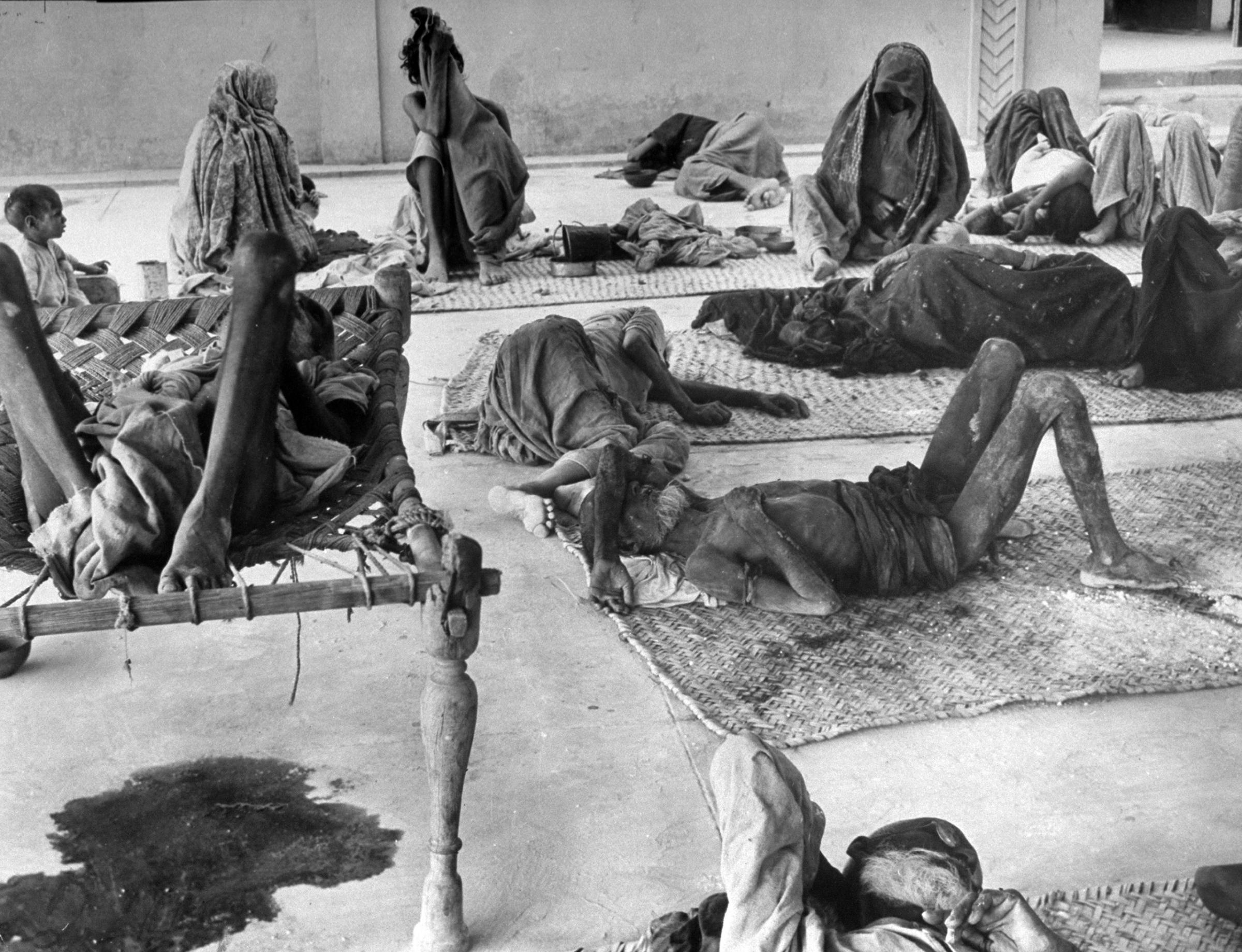
In the absence of a comprehensive visual record of the horrors of 1947 – in which at least one million people are estimated to have died – Bourke-White’s photographs have gained an iconic value. At Beas near Amritsar, she noted: “There were 17 corpses lying at the left of the railway tracks, the flies thick on the bloody stumps of arms.”
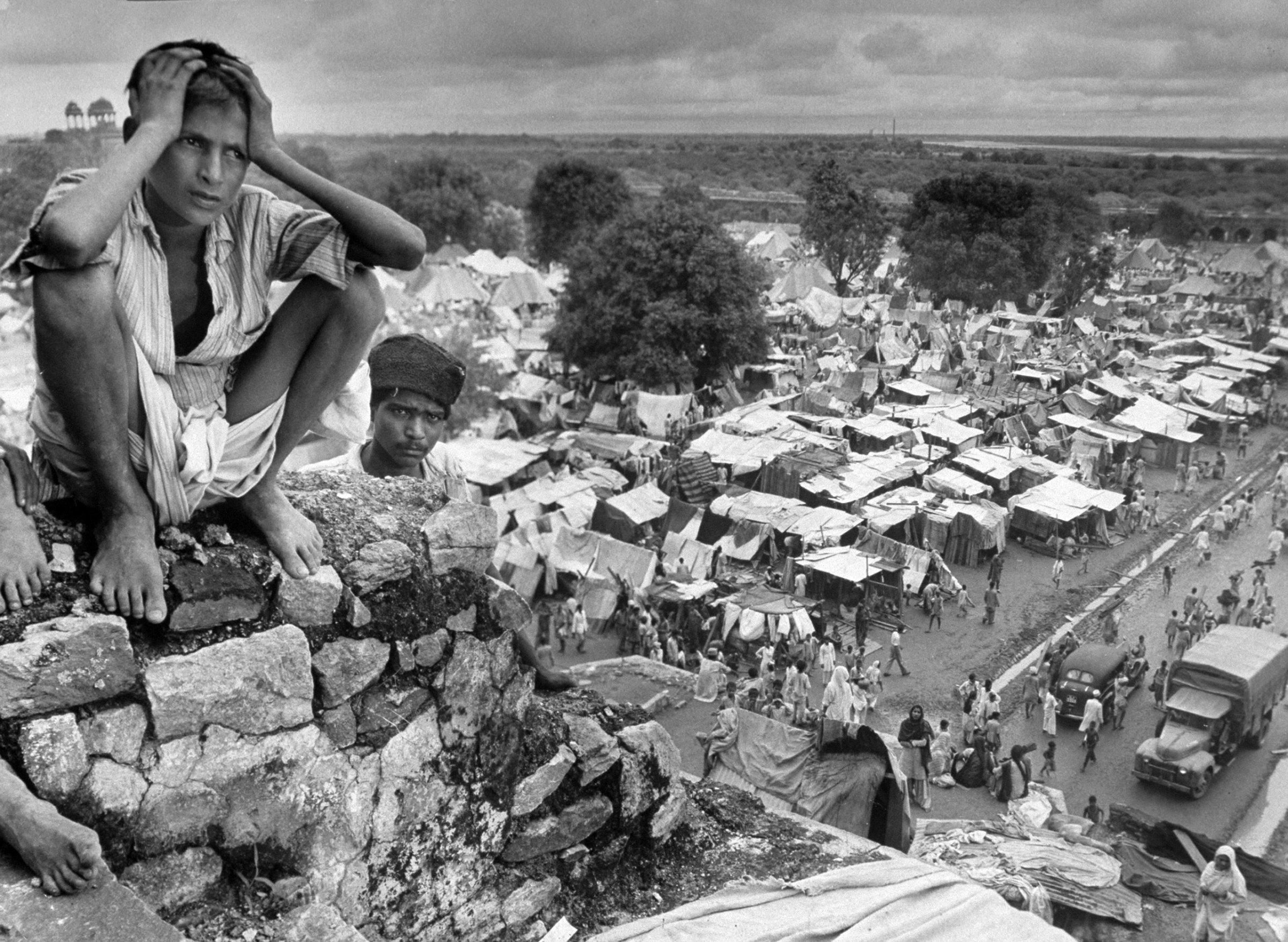
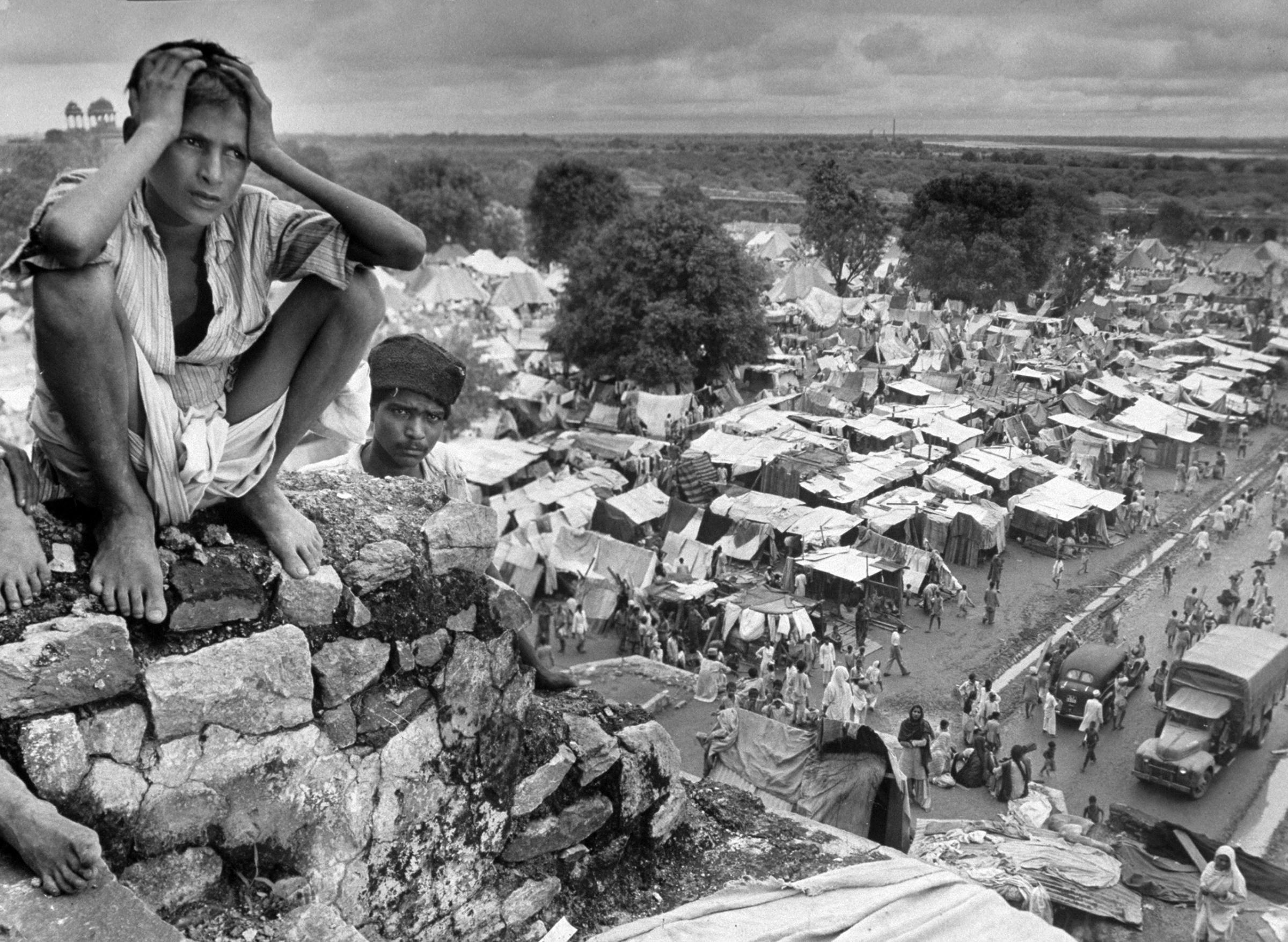
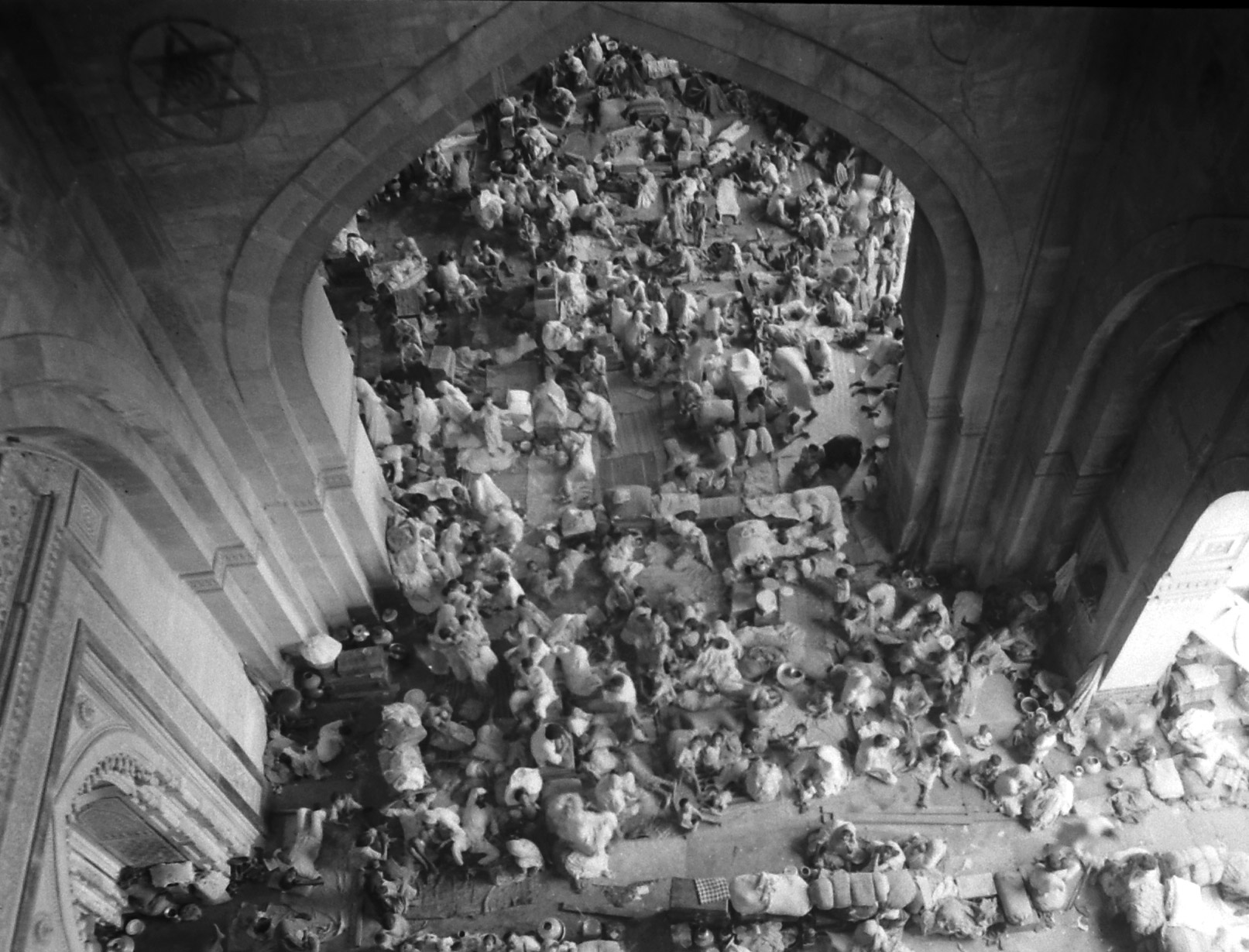
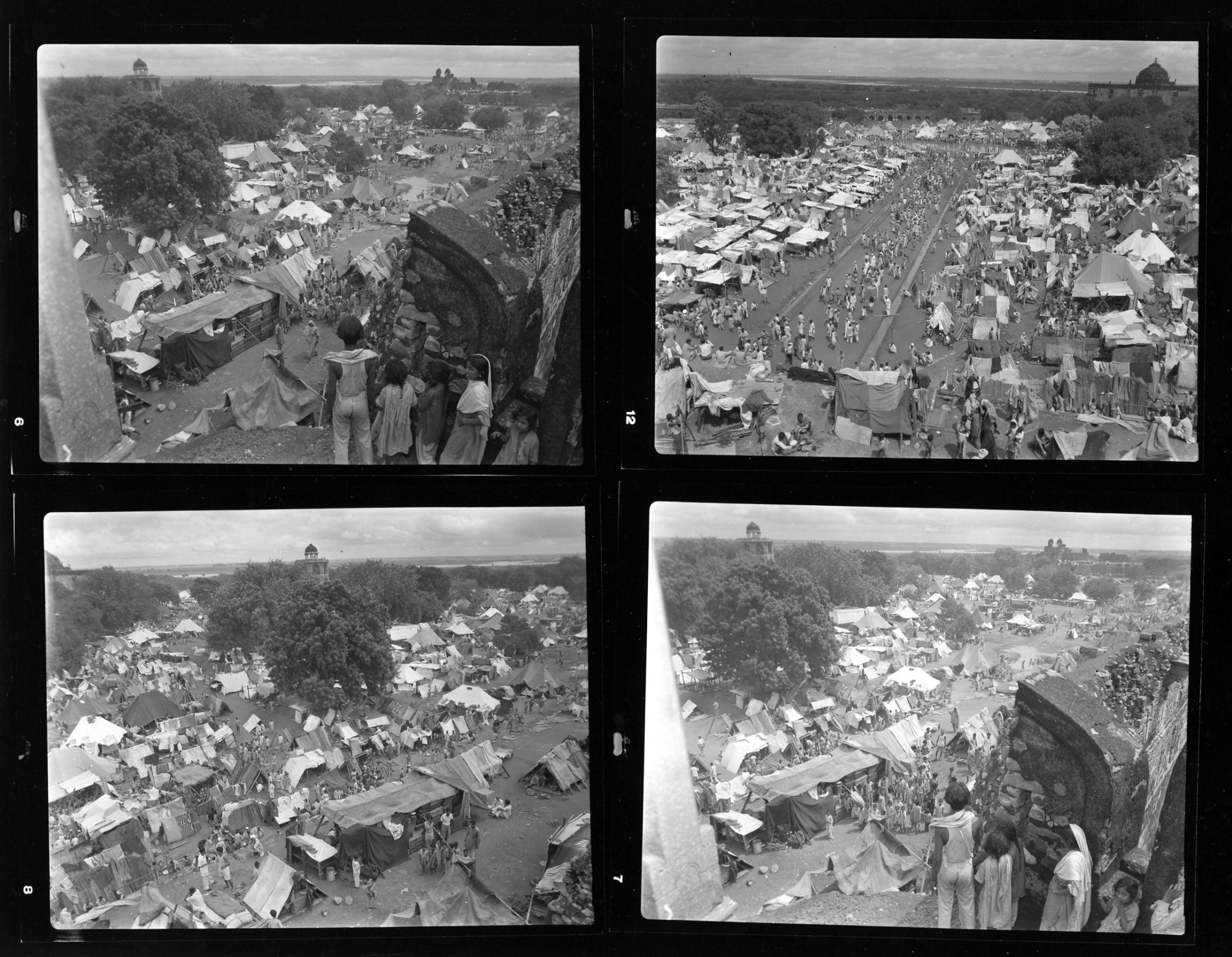
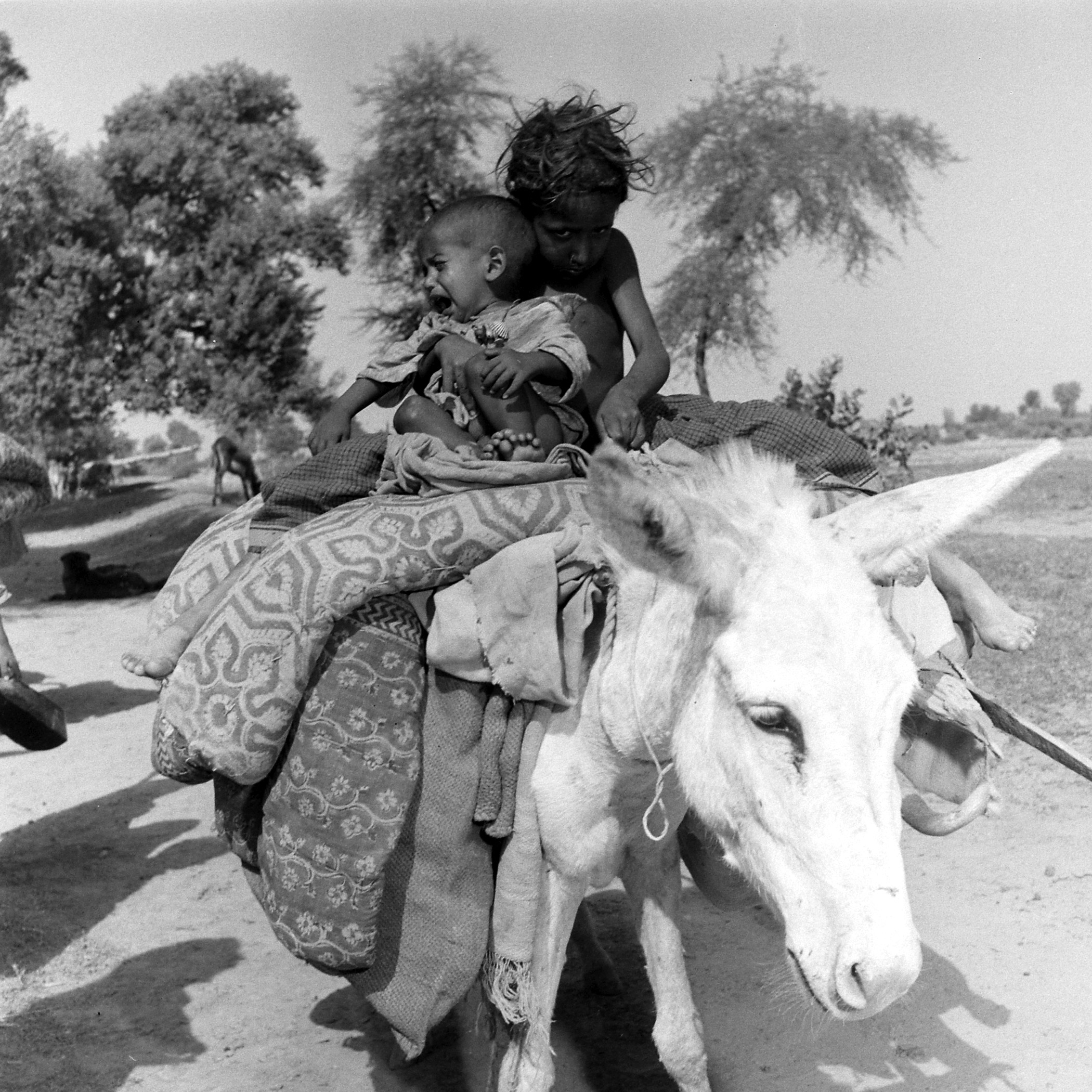
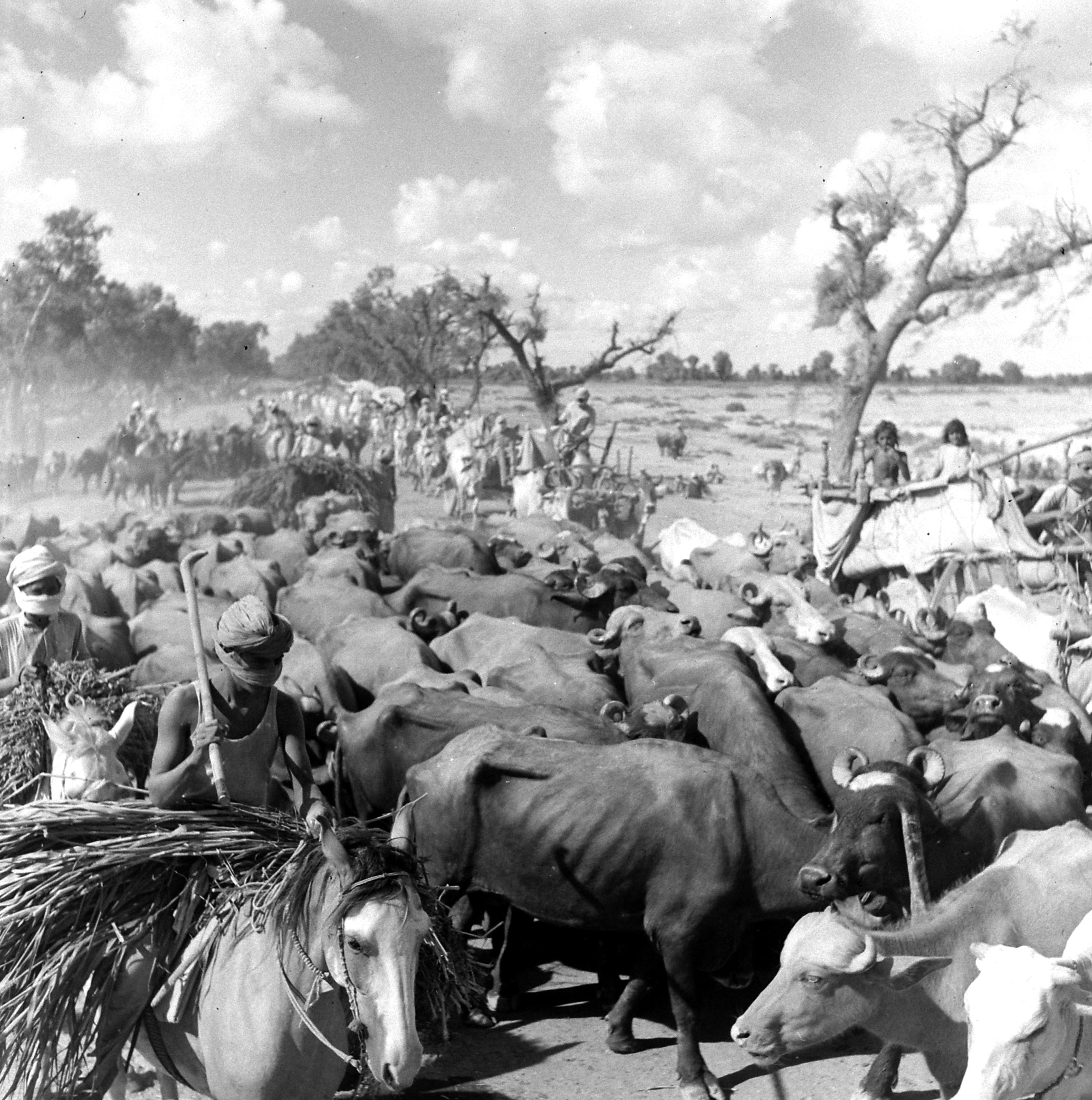
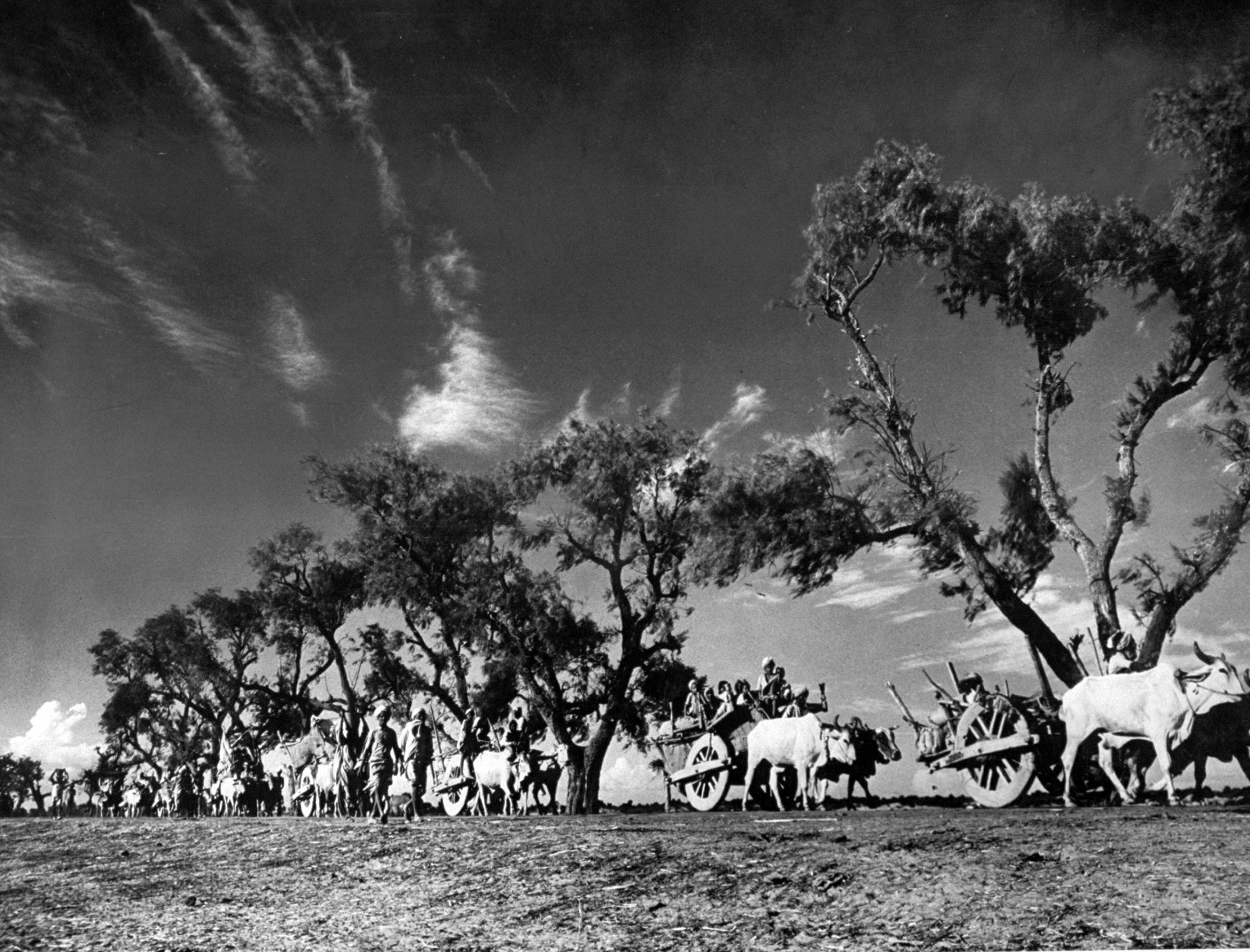
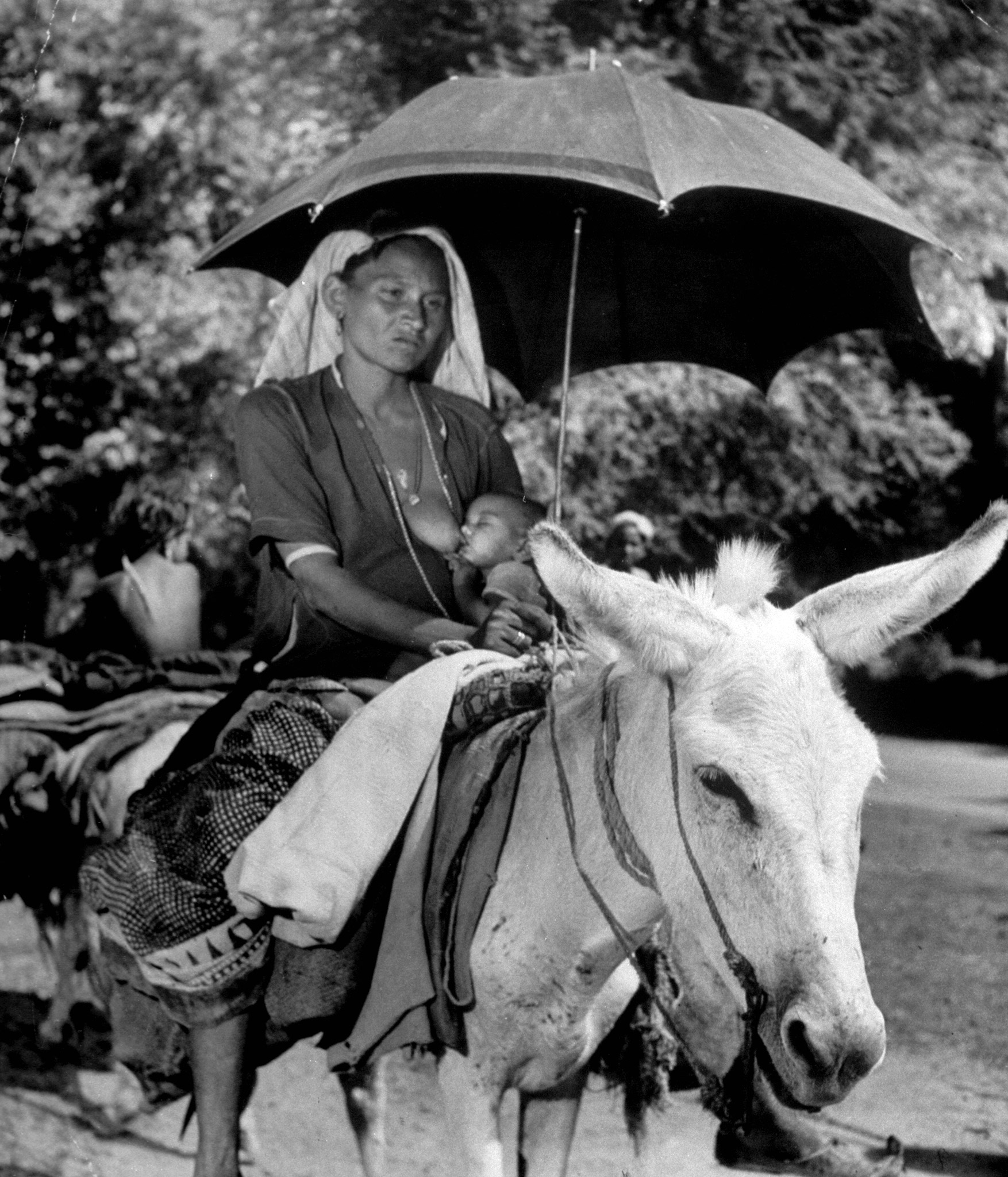
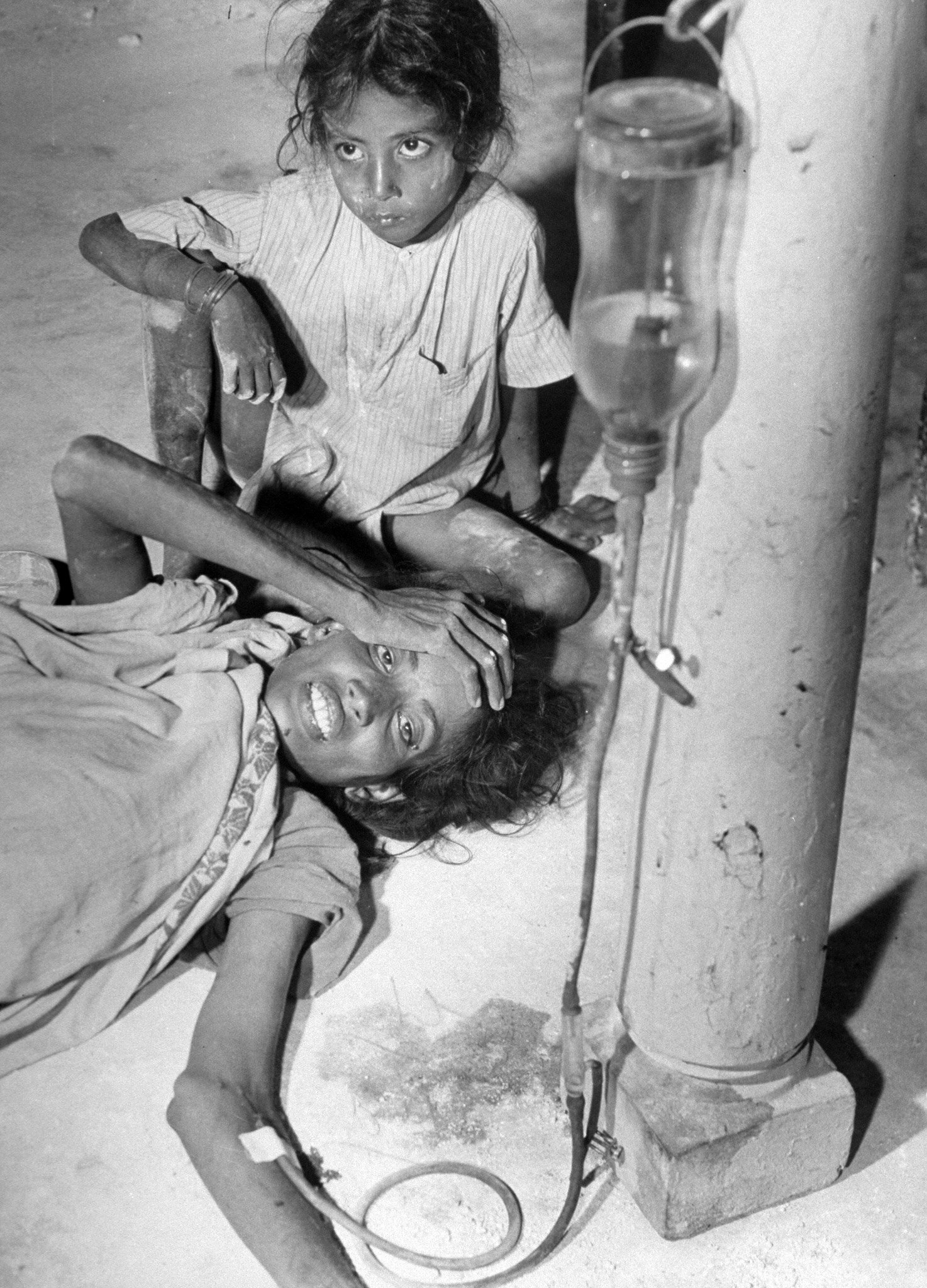
We ‘see’ the partition of India through her formalized, decolored, black-and-white images: kafilas or human caravans of refugees in Punjab, wooden bullock-carts piled with belongings, faces hovering between life and death, corpses in a river watched by fat vultures, an aerial shot of migrants sheltering in Qila-i-Kuhna mosque in Delhi, a cholera hospital in Kasur in the new Pakistan which, Bourke-White records here, was “pervaded with a sickening, sweetish smell.”
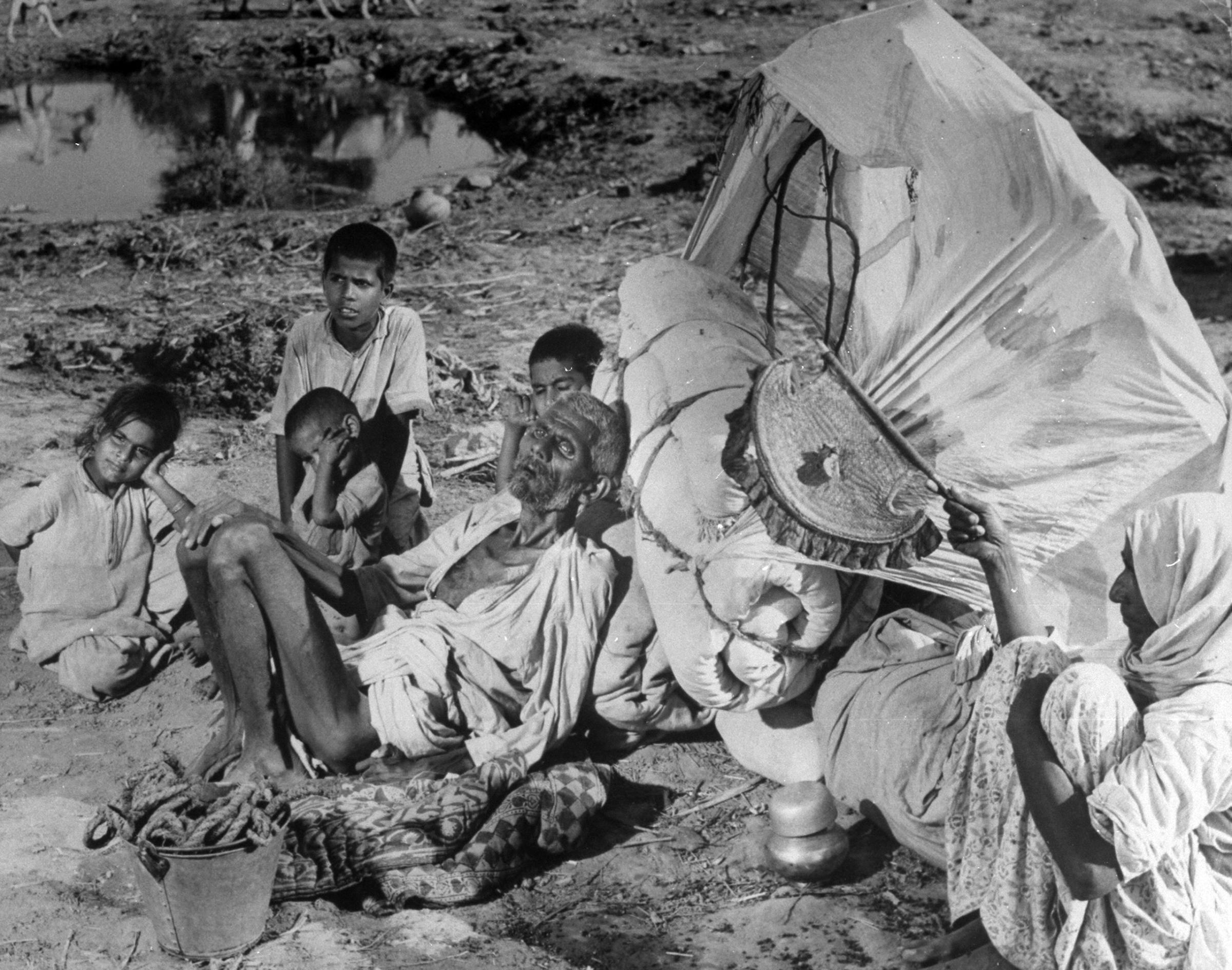
With the recovery of her notes from the LIFE archives, we are afforded, nearly 70 years later, little details that return some humanity to the nameless suffering figures. A famous photograph, of a shrouded corpse of a child who has died of starvation, comes back to life. We learn his name is Mansoor; he is 4 years old, and he is being buried near Lahore Cantonment railway station. The figures around him are his mother, father and grandfather. When their house in Delhi was looted, they had stayed at a refugee camp in Humayun’s Tomb. Then some good news came: because the father was a mechanic for the water and sewerage board in Delhi, the family would be able to board a ‘Pakistan Special’ train, bearing government employees. But in Punjab its passage was blocked, and for three days no food or water was allowed to the train. Mansoor died. Now he was being buried, and Margaret Bourke-White was a witness.
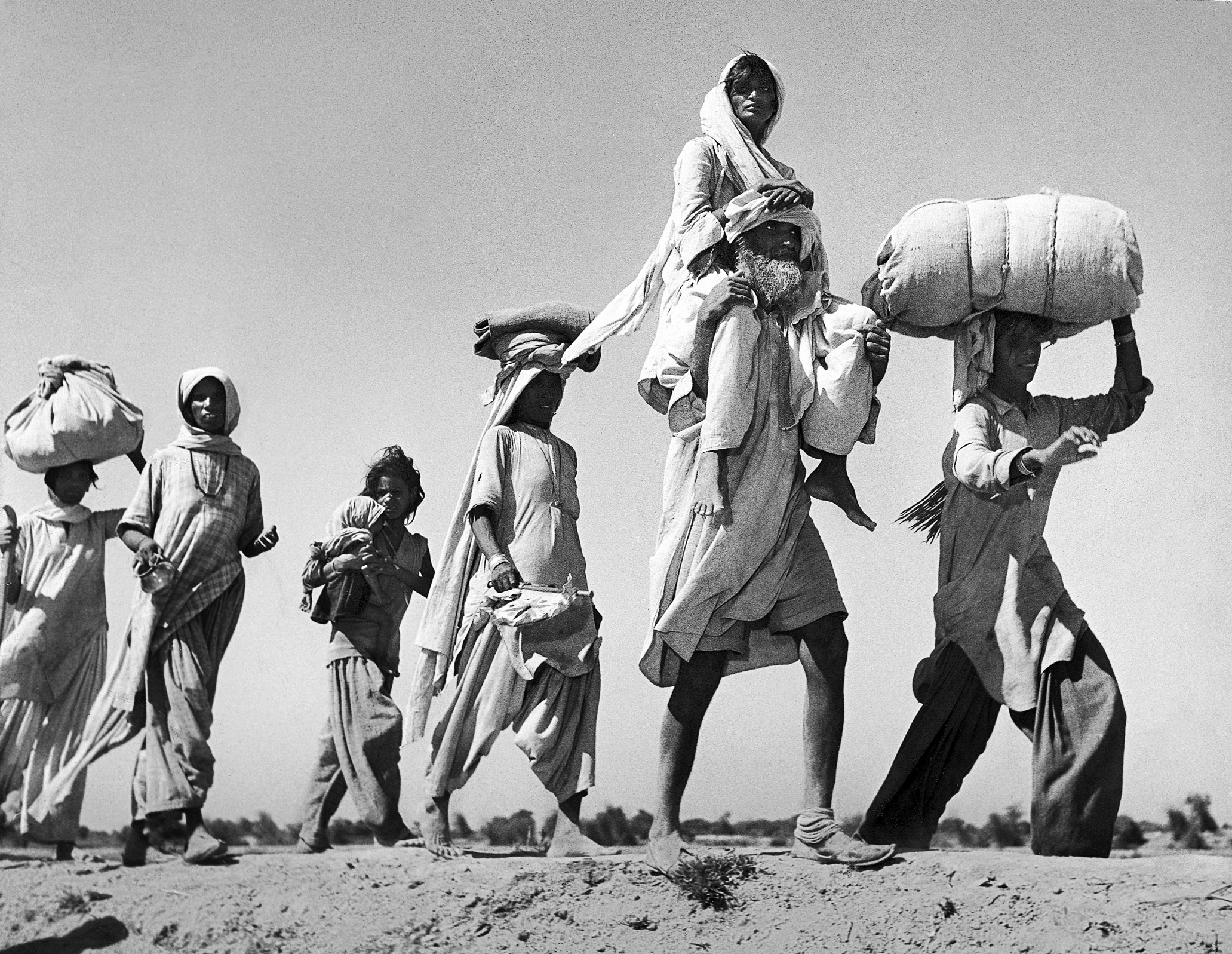
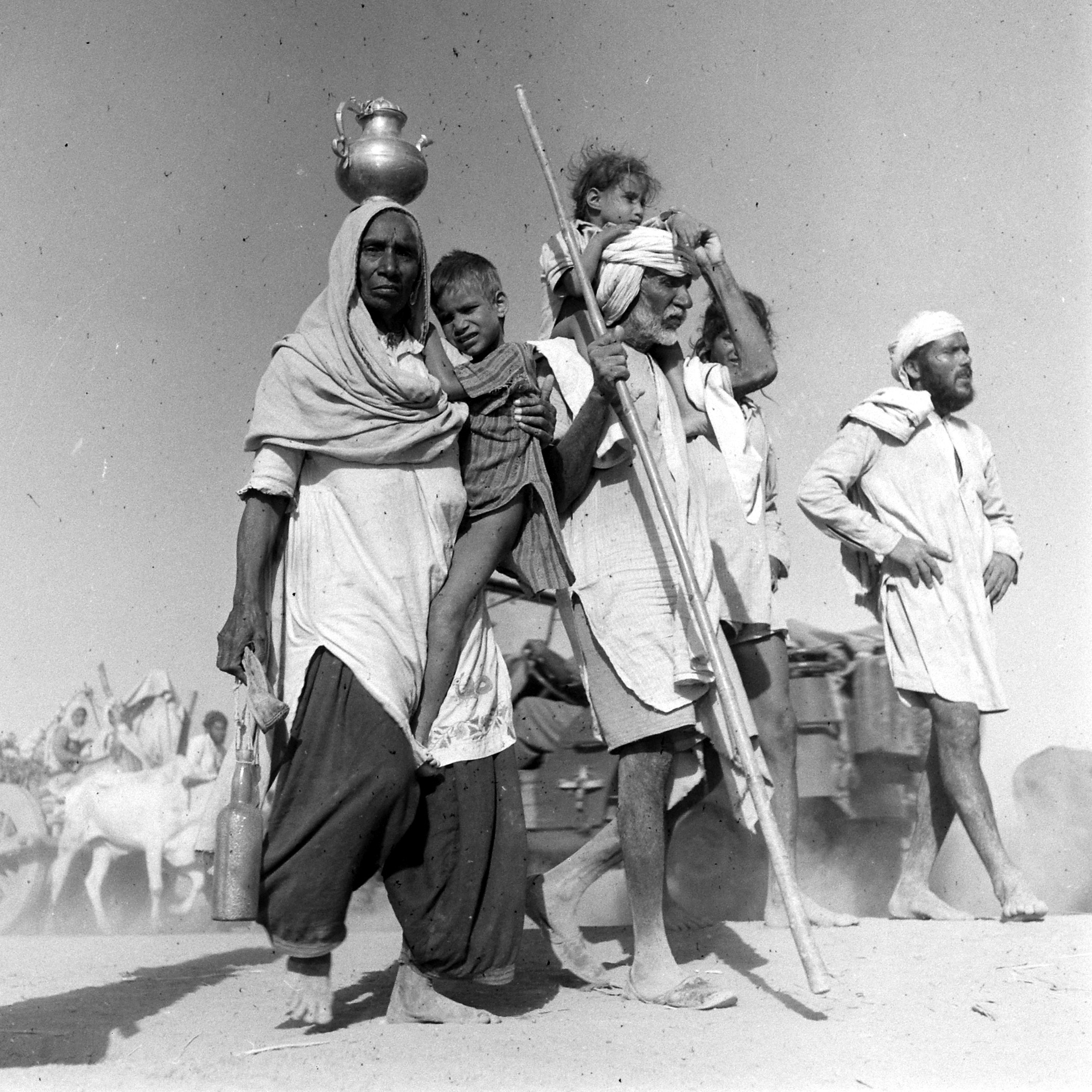
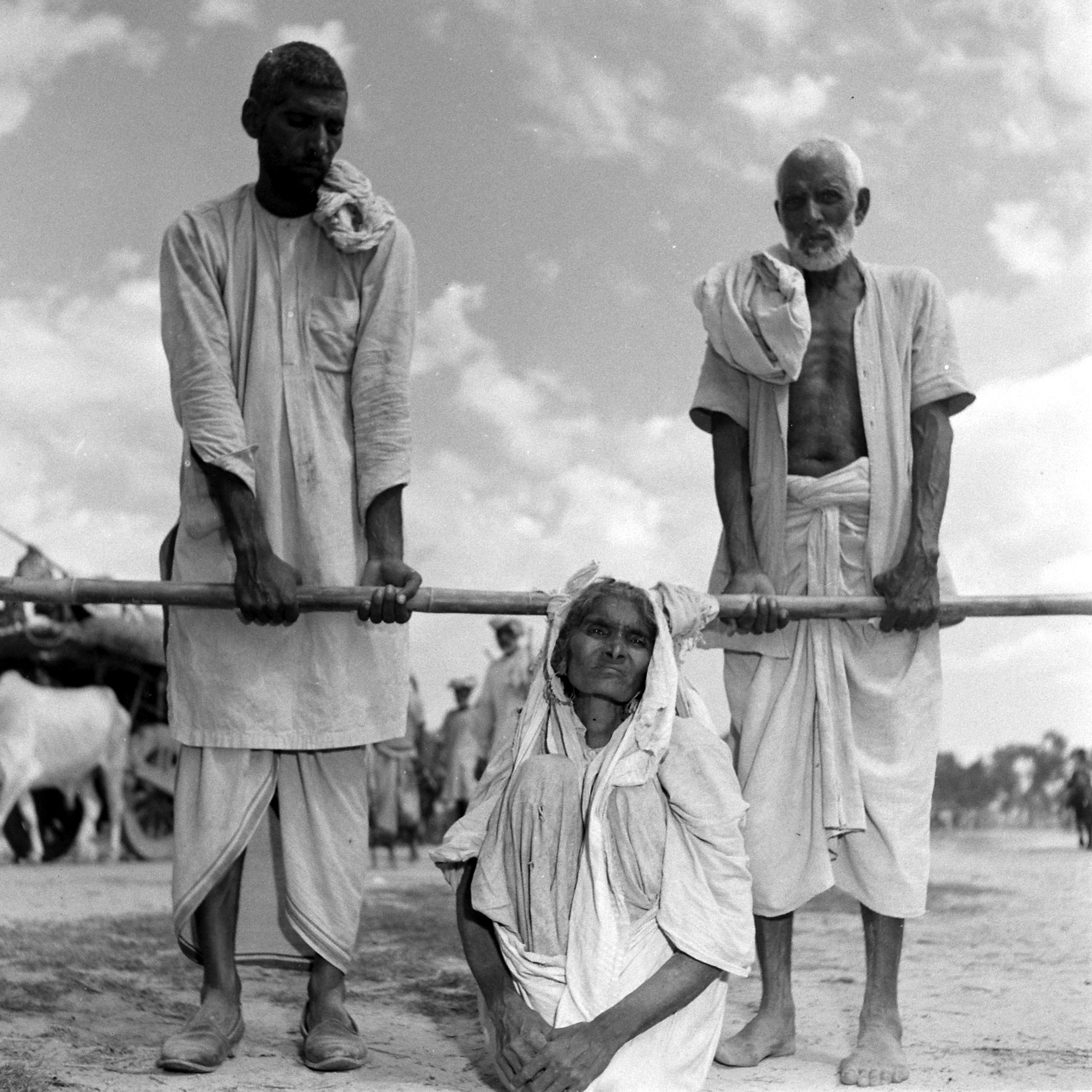
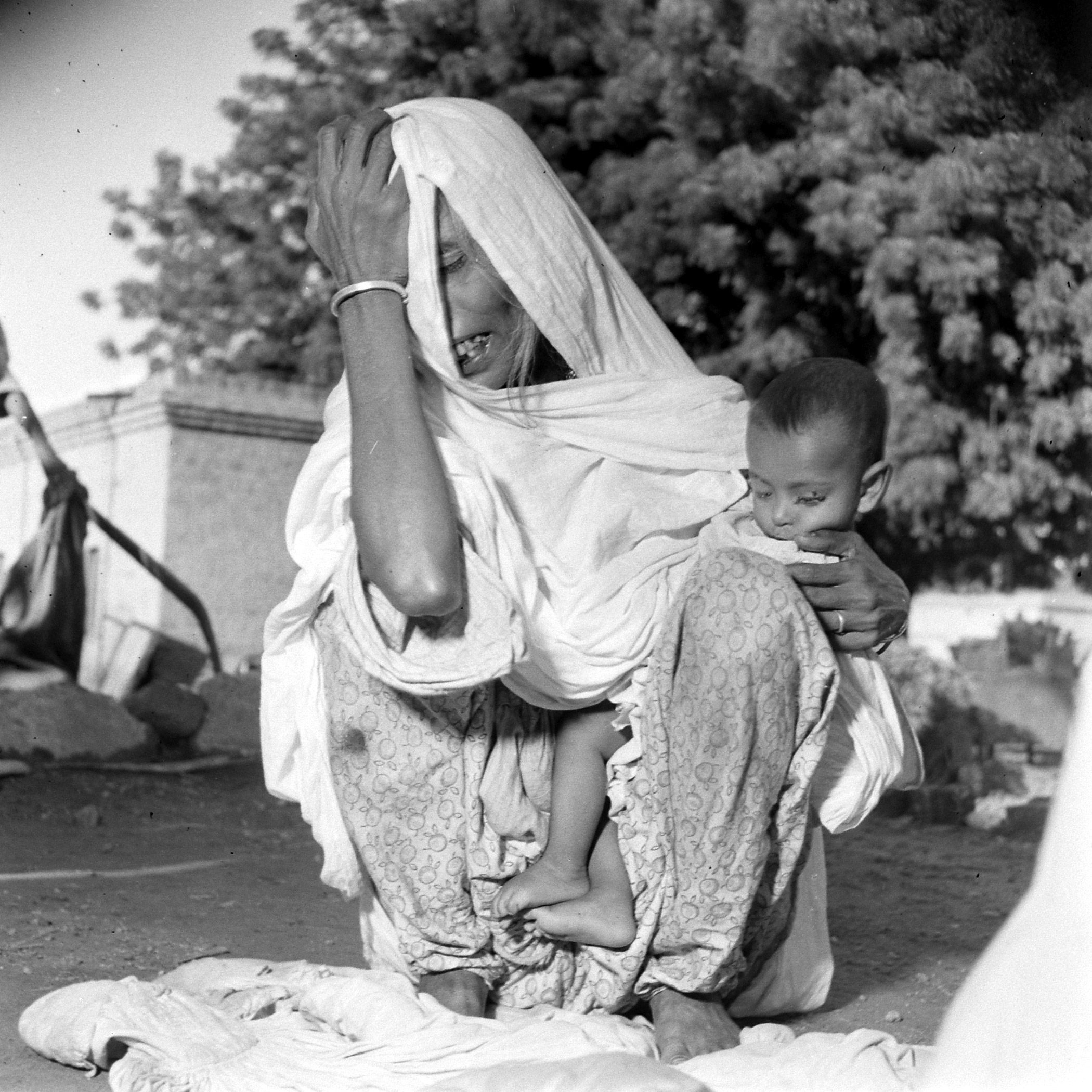
What of the stately image of a Sikh man bearing an ailing woman on his shoulders as they seek to walk to safety? From a biography of Bourke-White, we know this picture was to an extent staged. “We were there for hours,” Eitingon recalled years later. “She told them to go back again and again and again. They were too frightened to say no.” From the contact sheets, we can now see that an army vehicle was nearby, and the photograph was cropped. Bourke-White’s fierce determination to get just the pictures she wanted does not negate their quality, even if they were far from candid. From her scrupulously recorded notes, we learn this man was a farmer from Lyallpur district, now heading to India with his sick wife on his shoulders. Their kafila had been raided; 103 of its members were dead.
Across northern India and the nascent Pakistan, from Karachi to Bengal, many millions of people suffered in 1947 and the years that followed. Like all historical events, partition must be seen in the context of the time: politicians on all sides failed utterly to grasp the catastrophe they were creating. The British, bankrupt from World War II and exhausted by a dissolving empire, thought the solutions proposed by the Viceroy of India, Lord Mountbatten, and endorsed by nationalist Indian and proto-Pakistani statesmen, provided a constitutional answer.
What they had not foreseen was that terrified populations, when spurred by a new kind of identity politics, would flee or be driven from the lands in which they had lived for centuries. In that respect, the events chronicled in LIFE in 1947 seem very similar to ones that can still be seen in the world today.
Patrick French is the author of India: A Portrait and Liberty or Death: India’s Journey to Independence and Division, and a winner of the National Books Critics Circle Award.
Liz Ronk, who edited this gallery, is the Photo Editor for LIFE.com. Follow her on Twitter @lizabethronk.





















More Must-Reads from TIME
- Donald Trump Is TIME's 2024 Person of the Year
- Why We Chose Trump as Person of the Year
- Is Intermittent Fasting Good or Bad for You?
- The 100 Must-Read Books of 2024
- The 20 Best Christmas TV Episodes
- Column: If Optimism Feels Ridiculous Now, Try Hope
- The Future of Climate Action Is Trade Policy
- Merle Bombardieri Is Helping People Make the Baby Decision
Contact us at letters@time.com