The average U.S. life expectancy has hit its worst decline in 100 years and America’s standing is dismal among peer nations. But the average obscures a more complex story. The United States is facing the greatest divide in life expectancy across regions in the last 40 years. Research from American Inequality found that Americans born in certain areas of Mississippi and Florida may die 20 years younger than their peers born in parts of Colorado and California.
The decline is not occurring equally throughout the country. In the land of opportunity, millions of people are not even given a fair shot at life.
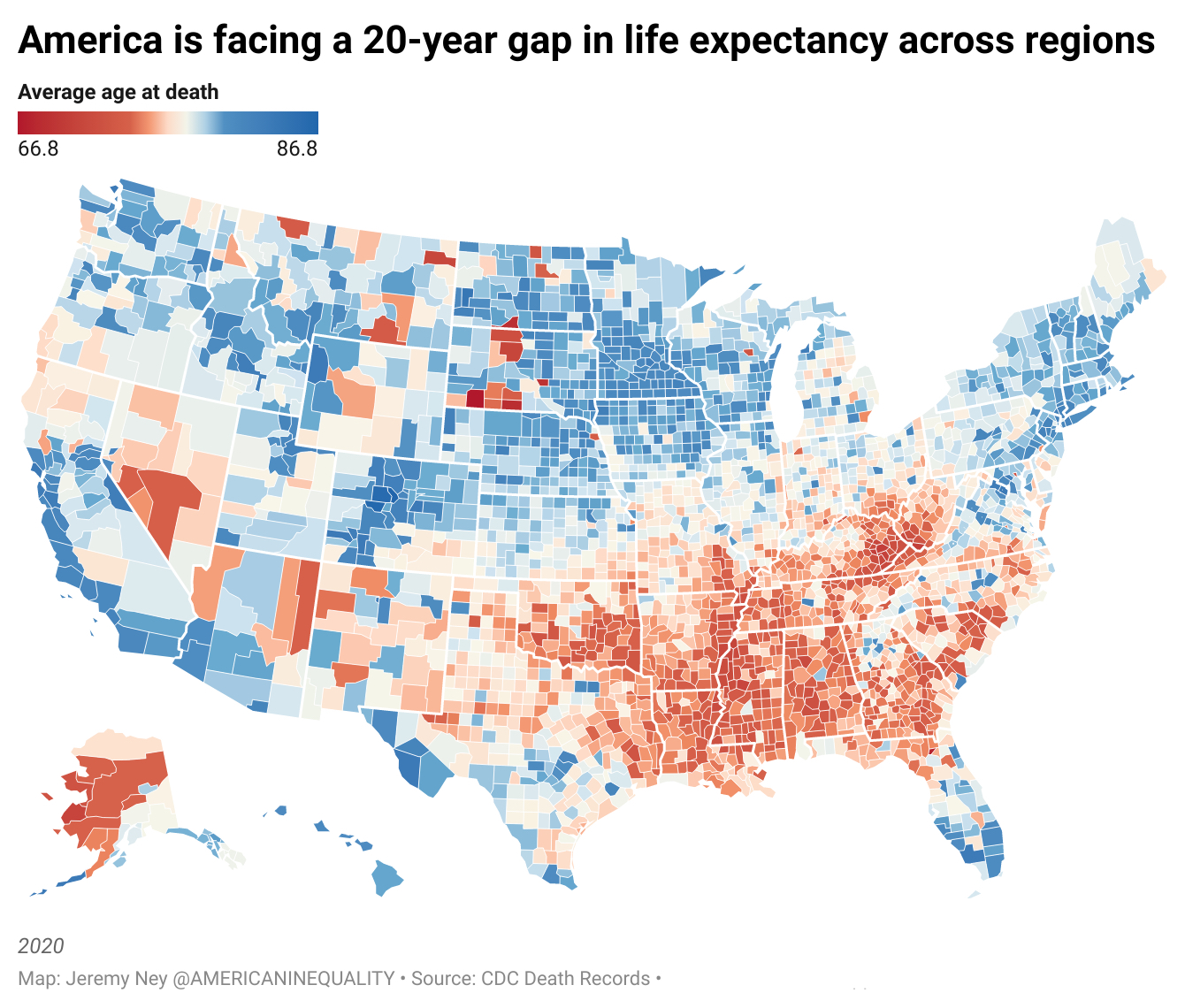
America is unique among wealthy countries when it comes to how young people die, and the trend is only getting worse. From 2019 to 2020, U.S. life expectancy declined by almost 2 years according to the Center Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the worst two-year decline since 1921-1923. When Covid hit, America experienced a larger decline in life expectancy than any other wealthy country. Life expectancy in America is now 76 years.
What is driving the differences in who lives and who dies in America? The answer is wealth, demographics, and location.
State policies tremendously influence life expectancy. Income support, medicaid expansion, stronger gun control, drug overdose prevention, and safe abortion access are among the drivers of regional divides in life expectancy. Overdoses kill more than 100,000 people each year. Guns kill more people than cars do. But digging into communities shed light on the country’s biggest issues.
More from TIME
Wealthier Americans live longer
Income is a major driver of higher life expectancies. In the wealthiest regions like Aspen, Colorado and Santa Clara, California, median household incomes reach the hundreds of thousands of dollars and Americans live to 87 on average, the highest in the country. But in poorer regions like or Owsley County, Kentucky or Union County, Florida, the median household income is $35,000 and life expectancy floats around 67 on average, the lowest in the country.
Our research has found a painfully high correlation between household income and life expectancy.
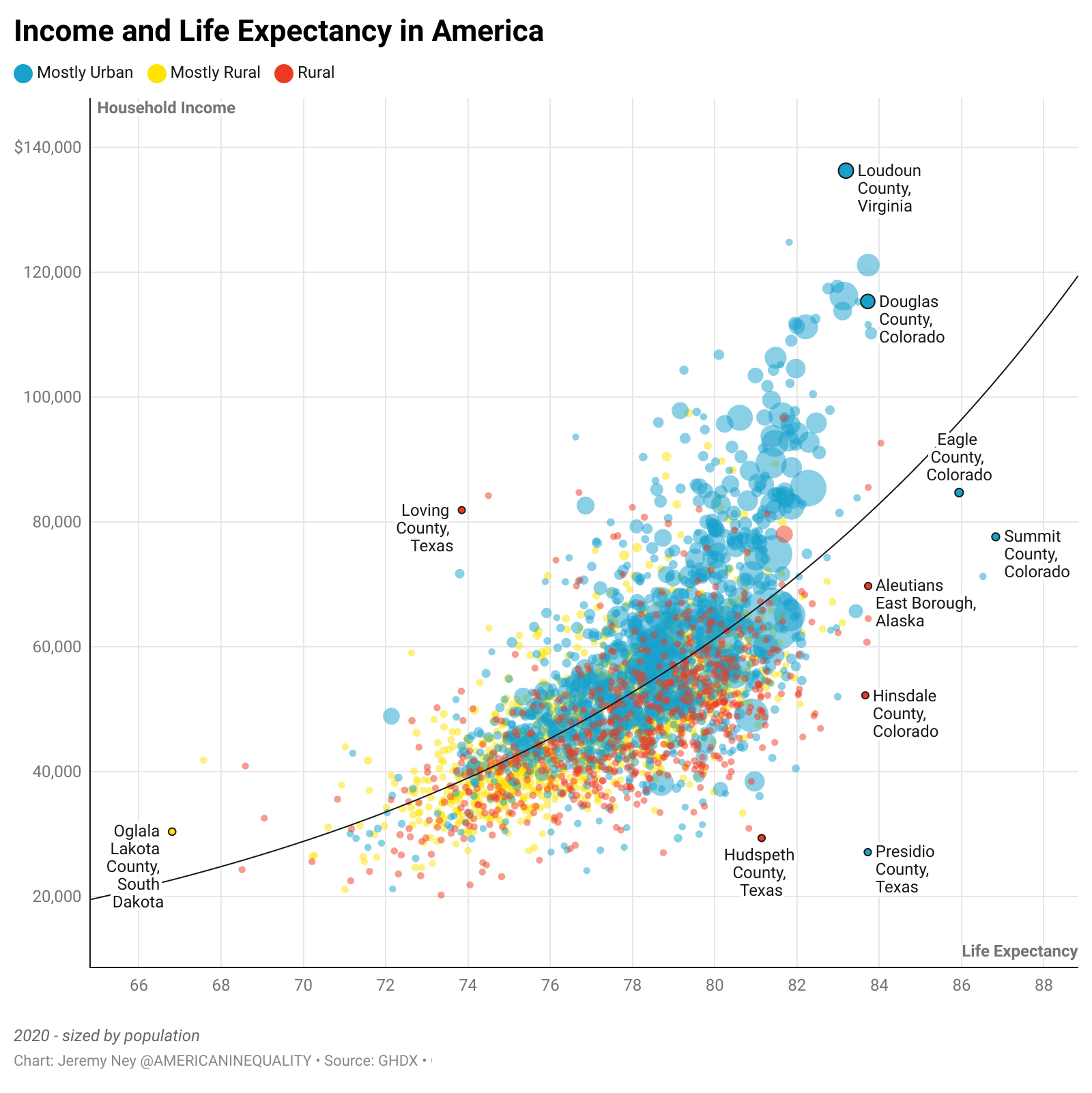
Poverty in America is not about income alone. Low-income communities, regardless of the state, are more likely to struggle with access to affordable healthcare; they are more likely to live near toxic sites and develop lung cancer; they are more likely to live in food deserts and wrestle with illnesses like heart disease and obesity; and they are more likely to die younger from drug overdoses.
Adequately addressing inequality in life expectancy requires looking across factors and working to improve these challenges for communities.
Black communities die younger
Thomas McGuire, professor of health economics at Harvard Medical School, explained, “In terms of health, there’s approximately a five-year penalty for being African-American compared to being a White male.”
Black Americans in every state have lower life expectancies than their White peers by 4 years on average. This is largely due to the lower-quality care that Black communities receive for conditions like cancer, heart problems, pneumonia, pain management, prenatal and maternal health, and overall preventive health.
Pemiscot County, Missouri represents this gap most clearly as it has one of the lowest Black life expectancies in America. In Pemiscot, Black residents die at 64 on average, effectively meaning that they will work until they die. 1 in 4 residents in Pemiscot is Black. Pemiscot has one public hospital that almost closed in 2013 and it’s one of the poorest counties in Missouri.
State policies make a big difference
States in the Deep South have lower life expectancies than states north of the Mason-Dixon line. These five factors may be the reasons why the residents of some states live far longer.
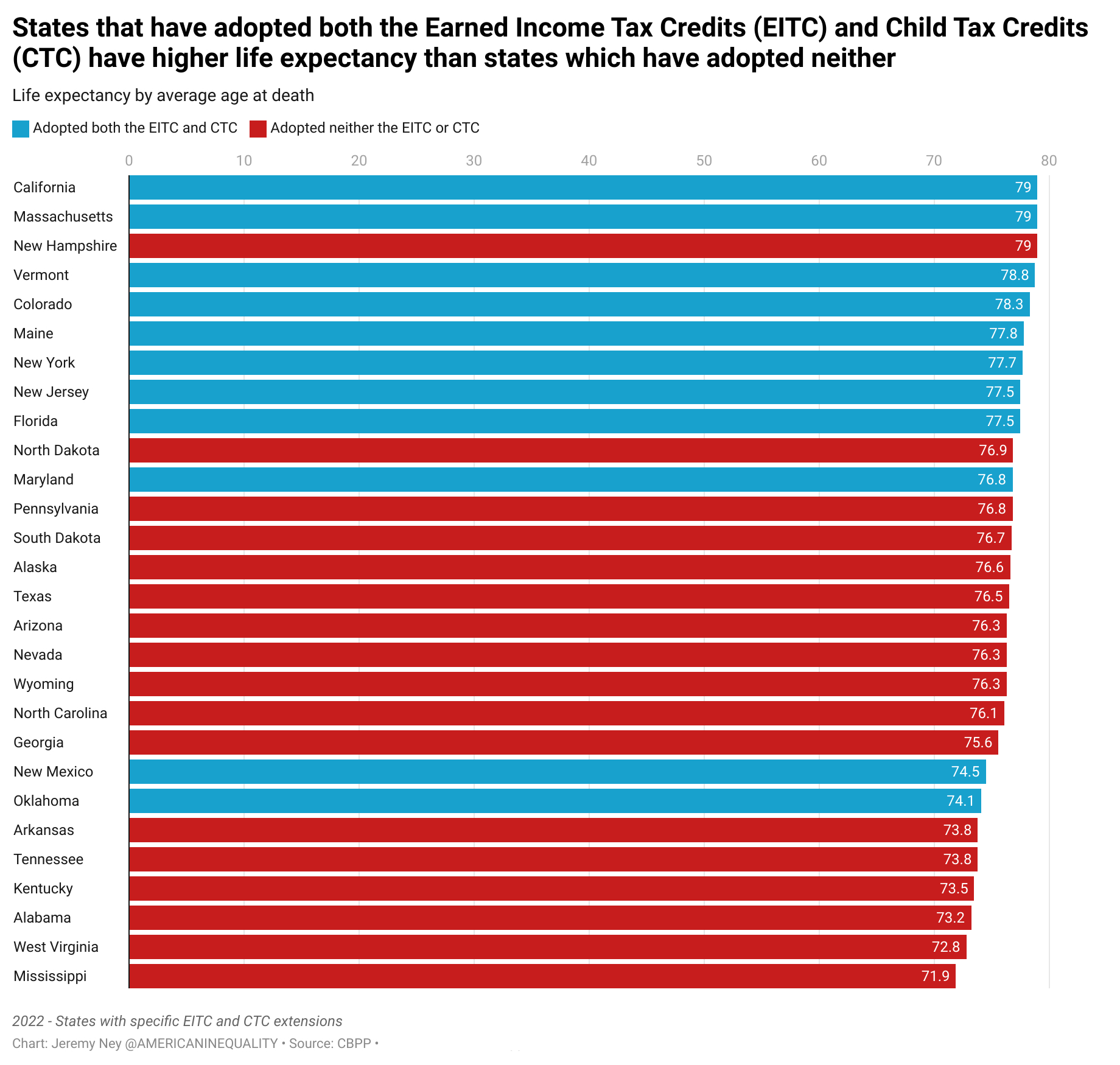
1. Expanding the EITC and CTC: More money means more time alive, and certain programs which put cash directly into low-income homes have improved life expectancy. The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Child Tax Credit (CTC) federally have been some of America’s most successful poverty alleviation programs, but 11 states have enacted their own CTC programs and 31 states have implemented their own EITC programs, putting more cash into the most needy homes. Residents in states that have adopted both the EITC and CTC tend to live 2 years longer than states which have implemented neither. This may even be more cost effective at increasing life expectancy than many other policies. These programs are designed to support children, too.
2. Medicaid Expansion: States that expanded Medicaid saved more than 200 lives per every 100,000 people and decreased the risk of premature death by roughly 50% for older adults who gained coverage. As Nobel-Prize wining economist Paul Krugman explained, “Some of the poorest states in America, with the lowest life expectancy, are still refusing to expand Medicaid even though the federal government would cover the bulk of the cost.” Such individuals in turn are therefore at the mercy of policies that differ state to state.
3. Gun Control: Stronger gun control measures in states also improve life expectancy. The South, which has some of the most lenient gun control measures, lost 5.7 million years of life expectancy in the period 2009-2018 from firearm related deaths. Conversely, Northeastern states, which tend to have much stronger gun control measures like background checks and secure storage laws, had one-fifth the loss in life expectancy. Guns are now the #1 killer of children in America and 1 in 25 American 5-year olds now won’t live to see 40, largely due to guns. If we stopped these deaths, it would effectively add 3 years of life to every 5-year old in the South.
4. Drug Overdose Prevention: States that introduced policies to prevent drug overdose deaths saw life expectancies increase by 11%. The CDC estimates that half of all the unintentional deaths last year that took people’s lives too early were attributed to drug overdoses. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved Naloxone to be sold over the counter at pharmacies, which could help close the state-by-state gap. In the meantime, McDowell County, West Virginia has one of the lowest life expectancies in the country and has the highest rate of opioid overdoses in the country.
5. Abortion Access: Lastly, while the data has not fully revealed the impact of the Supreme Court’s ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson, this decision may drive further divides in life expectancy for Southern states that have in turn limited abortion access. Arkansas has a maternal mortality rate that is 50% higher than the national average. In Mississippi, it is 75x more dangerous for women to carry a pregnancy to term than to have an abortion due to poor healthcare. Mississippi has the lowest life expectancy in America at 71. Causing more women to carry a pregnancy to term may increase deaths of mothers in their 20s-40s.
The 20-year gap in life expectancy across regions tells story of America. The divide is deeply interwoven with healthcare, housing, race, gender, location, education, and more. But improving life expectancy across regions in possible and it starts with state legislatures. States can learn from each other about what has worked best and implement new policies with proven effectiveness. Data will be the driving force for finding patterns of inequality and leading change-makers towards solutions that engender equality.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at letters@time.com
