It’s not often astronomers are completely stumped—especially when it comes to Mars. The planet that once held nothing but mysteries has been yielding up more and more of its secrets, thanks to the storm of probes we’ve sent its way over the decades, including the seven that are now orbiting it or trundling about on its surface.
But something’s up with Mars at the moment—or at least something was up not long ago—and nobody seems able to explain it. That’s the beats-me conclusion a team of investigators reached in a new paper in Nature, when they attempted to explain a freakish plume that appeared in the Martian atmosphere in March and April of 2012, and might have occurred in 1997 as well.
The newest plume, which rose an unprecedented 155 miles (250 km) high in the Martian sky, was first observed by Wayne Jaeschke, an amateur astronomer in West Chester, Pa. on March 12, 2012. He sent the word out across the amateur astronomer community and soon reports were coming back that yes, other backyard sky-watchers were seeing the same thing. The plume lasted for 11 days and then recurred on April 6, this time hanging around for 10 days. Both phenomena appeared in the same spot in Mars’s southern hemisphere.
Plumes aren’t unheard of on Mars. The planet does have an atmosphere, after all—albeit one only 1% the thickness of Earth’s—and both dust and ice crystals can swirl up into the sky. Aurorae may also appear when charged particles streaming in from the sun interact with the planet’s magnetic field, which can create a plume-like effect.
But ice crystals have never been observed to climb above an altitude of 62 miles (100 km). Aurorae occur higher in the Martian sky, but at a maximum of 80 miles (130 km), they fall short too. And dust storms don’t even come close.
But those three are the only known explanations for what Jaeschke and the others saw—or at least the only known ones—and the mere fact that dust or ice or aurorae have never behaved this way before does not mean that they can’t. So a team of researchers led by Agustín Sánchez-Lavega of the University of the Basque Country in Bilbao, Spain, decided to put all three theories to the test.
Photos from the Curiosity Rover’s First 2 Incredible Years on Mars
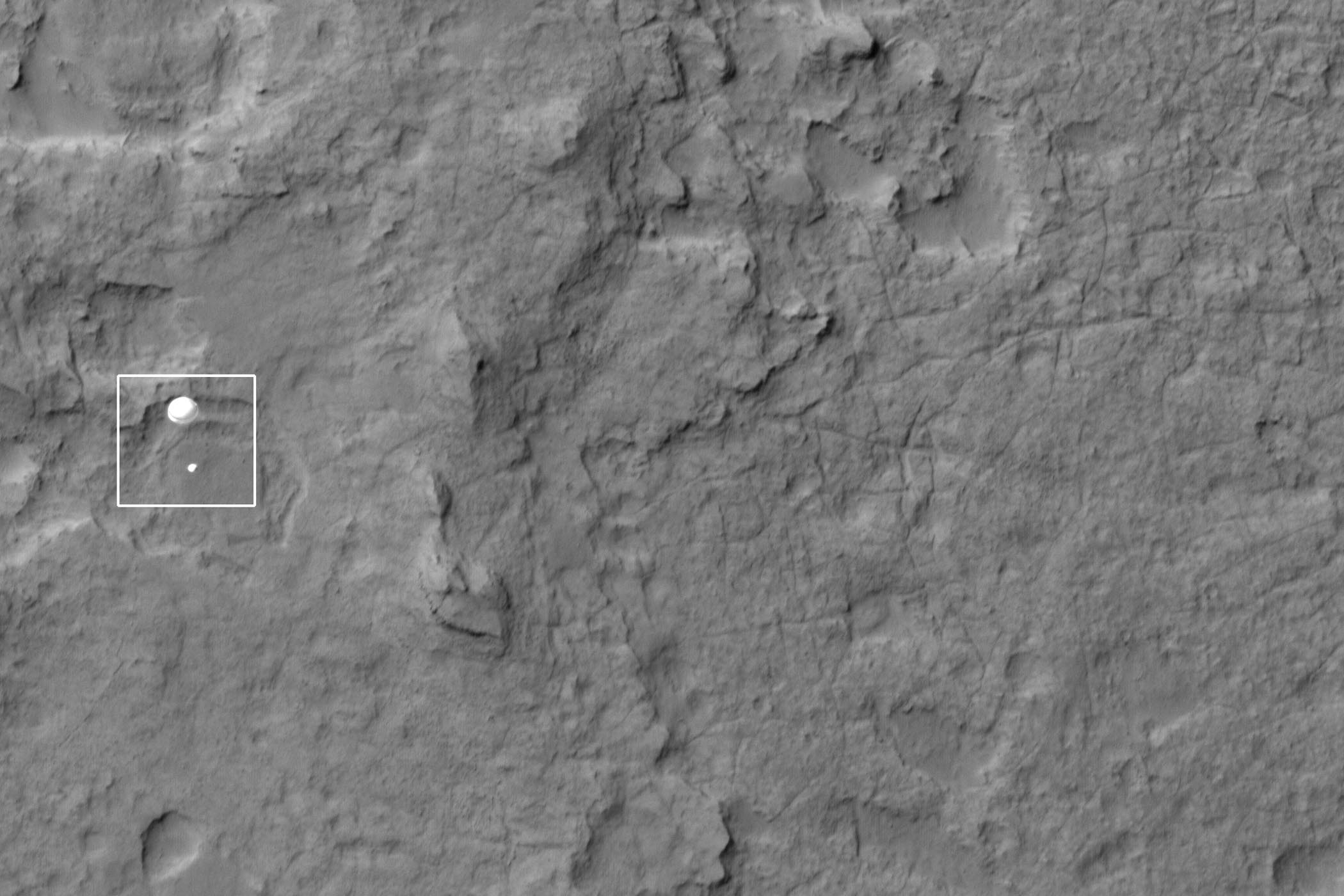













The investigators began their work by studying not just the images of the plumes but also roughly 3,500 pictures of Mars captured by amateur astronomers around the world from 2001 to 2014, as well as a series of shots taken by the Hubble space telescope from 1995 to 1999, when it was giving the Red Planet a good going-over. None of these pictures showed anything similar to the 2012 phenomena except for a single shot taken by Hubble on May 17, 1997, which did show a similar plume in a similar spot.
Ice crystals—whether made of water or carbon dioxide—were easy for the researchers to rule out. In addition to the altitude problem, the atmosphere would have to be significantly colder than it typically is at the height at which the plume was observed, and if the crystals were water ice, conditions would also have to be far wetter than they ever get so far above ground. The reflectivity of the plume was similar to what would be expected if light were bouncing off of ice crystals, but that doesn’t fix the other problems.
Dust was even less plausible. In this case, the reflectivity was all wrong and while so called “rocket dust storms” could, in theory blow dust to unprecedented altitudes, no such gales were observed on Mars at the time of the plume in 2012. All this was true of the 1997 plume as well.
And as for aurorae? They struck out too. Incoming solar energy was too weak at the time to put on such a sky show, and even if it had been, the plumes were too dim in the ultraviolet frequencies to be aurora-related.
The astronomy community as a whole seems untroubled that the study concluded with what amounts to a peer-reviewed who knows? “The observation is a big surprise,” said French astronomer Aymeic Spiga, in a statement put out by Nature. “Another puzzle on Mars!” And happily, the conspiracy community has not yet been heard from—whispering on as they did about the mysterious face on Mars photographed by the Viking 1 spacecraft in 1976, which turned out to be nothing more than a mound in the planet’s Cydonia region cast in evocative shadows on the day it was photographed. By 1998, the Mars Global Surveyor revealed that the formation had largely eroded away.
The plumes, if they prove anything, are merely one more sign that we have a great deal to learn about our close planetary neighbor. Life may or may not exist on Mars, but cosmic puzzles surely do.
Read next: Astronauts Vying for One-Way Ticket to Mars May Be on Reality TV
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- The Revolution of Yulia Navalnaya
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- What's the Deal With the Bitcoin Halving?
- If You're Dating Right Now , You're Brave: Column
- The AI That Could Heal a Divided Internet
- Fallout Is a Brilliant Model for the Future of Video Game Adaptations
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Jeffrey Kluger at jeffrey.kluger@time.com